.
Sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive and strong mineral acid that is widely used in industry for various applications, such as the production of:
.
- fertilizers
- detergents
- chemicals
.
.
Its chemical formula is H2SO4, and it is composed of hydrogen, sulfur, and oxygen atoms.
.
Sulfuric acid is a colorless, odorless liquid that can cause severe burns on contact with skin and eyes.
.
It is also a highly reactive substance that can react with many other chemicals, making it an important reagent in chemical synthesis.
The production of sulfuric acid is associated with several environmental issues, which are explained in the next parts of this article.
.
Air Pollution
.

.
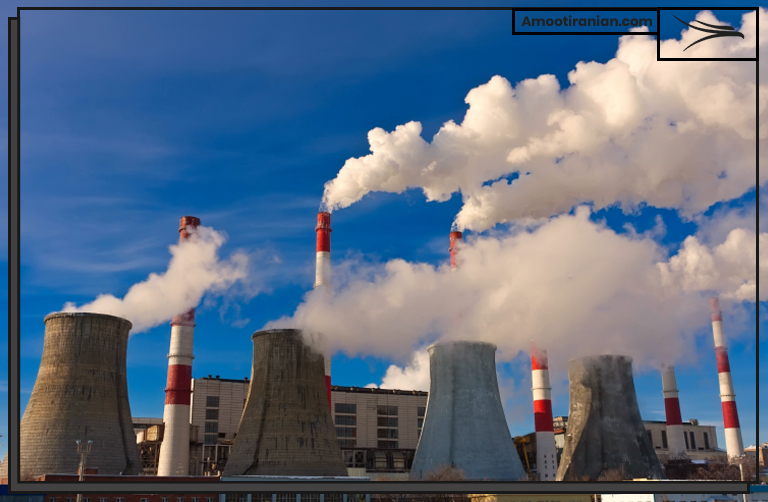
The process of sulfuric acid production releases large amounts of sulfur dioxide (SO2) into the air. SO2 is a colorless gas with a pungent odor.
It is a chemical compound composed of sulfur and oxygen molecules.
SO2 is a byproduct of many industrial processes, such as the combustion of coal and oil in power plants and the production of paper, chemicals, and metals.
SO2 is a major contributor to acid rain and can cause respiratory problems when inhaled. Some of these problems are:
.
1_Respiratory Problems
Exposure to high levels of SO2 can cause respiratory problems, particularly for individuals with asthma and other pre-existing lung conditions. It can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, leading to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
2_Acid Rain
SO2 contributes to the formation of acid rain when it reacts with water, oxygen, and other chemicals in the atmosphere. Acid rain can have harmful effects on crops, forests, and aquatic life by altering soil and water chemistry.
3_Industrial Corrosion
SO2 can react with metal surfaces and cause corrosion, leading to damage to industrial equipment and infrastructure.
4_Environmental Damage
SO2 emissions can have harmful effects on the environment, including damage to vegetation, loss of biodiversity, and reduced soil fertility.
5_Global Warming
SO2 is a greenhouse gas and can contribute to global warming by trapping heat in the atmosphere.
.
Water Pollution
.

.
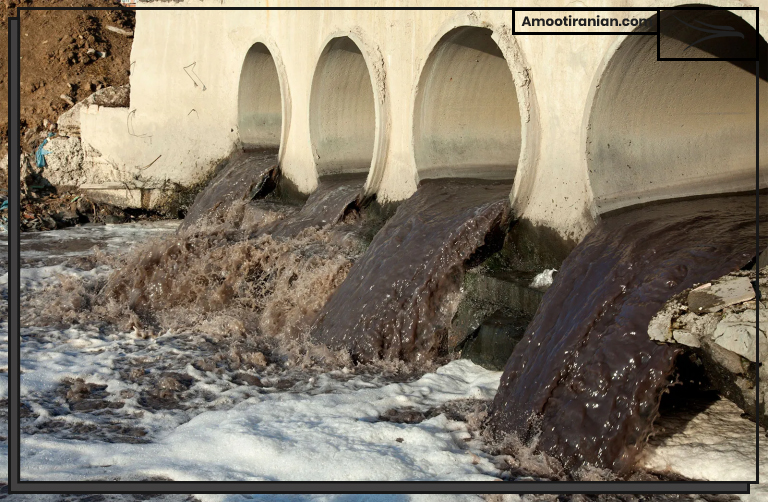
The disposal of waste sulfuric acid can lead to water pollution. Sulfuric acid can contaminate water sources, making them unfit for human consumption and harmful to aquatic life.
If sulfuric acid is not properly stored or disposed of, it can leak or spill into the environment, contaminating water sources and making them unsafe for human consumption.
Sulfuric acid can react with water to form sulfuric acid solution, which is highly acidic and can lower the pH of water bodies, making them acidic and harmful to aquatic life. This can lead to fish kills, algal blooms, and other negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
In addition to harming aquatic life, sulfuric acid can also have negative impacts on human health. If people drink or swim in water contaminated with sulfuric acid, it can cause skin irritation, burns, and respiratory problems. Long-term exposure to sulfuric acid in drinking water can also increase the risk of cancer.
To prevent water pollution from sulfuric acid, industries that use this chemical are required to have proper waste management systems in place, which includes treating the acid before it is released into the environment.
Treatment methods can include neutralization, which involves adding a base to the acid to raise the pH and reduce its acidity, or using chemical processes to break down the acid into less harmful compounds.
Overall, it is important to properly manage and dispose of waste sulfuric acid to prevent water pollution and protect human health and the environment.
.
Energy Consumption
The production of sulfuric acid requires large amounts of energy. This can lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to climate change.
Sulfuric acid is commonly produced through the Contact Process, which involves the oxidation of sulfur dioxide (SO2) to sulfur trioxide (SO3) using a catalyst, followed by the reaction of SO3 with water to form sulfuric acid.
The production of sulfuric acid requires large amounts of energy in the form of heat, which is typically generated by burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
This combustion process releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of sulfuric acid production can also contribute to other environmental issues, such as air pollution and acid rain.
To reduce the energy consumption and environmental impact of sulfuric acid production, industries have implemented a number of measures, including:
.
- Energy Efficiency: Improving energy efficiency through process optimization, waste heat recovery, and the use of high-efficiency equipment and technologies can help to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Alternative Energy Sources: Switching to alternative energy sources such as renewable energy (e.g., solar, wind, hydro) or biofuels can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions from sulfuric acid production can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Recycling and Recovery: Implementing recycling and recovery systems can help to reduce waste and improve resource efficiency in sulfuric acid production.
.
Overall, reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions from sulfuric acid production is essential to mitigate the effects of climate change and ensure sustainable development.
.
Land Degradation
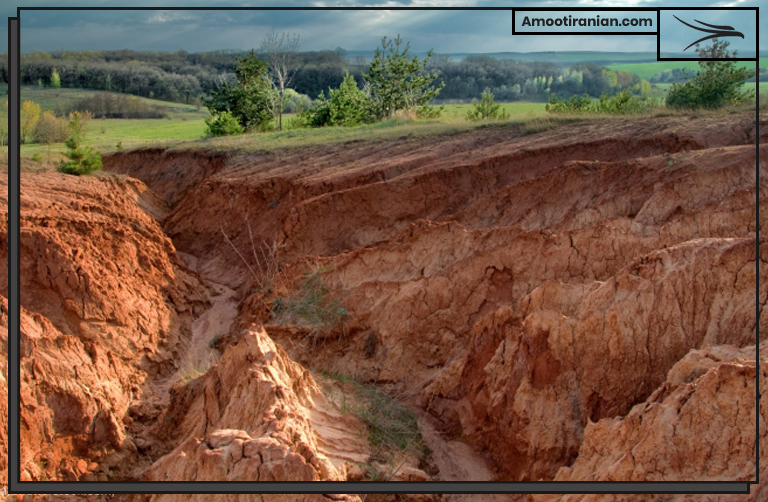
Improper disposal of waste sulfuric acid can lead to land degradation, which is the process by which the quality of soil deteriorates, making it less productive and less able to support plant growth. Sulfuric acid is highly corrosive and can react with soil components, altering its chemical and physical properties.
When sulfuric acid is dumped on the ground, it can react with the minerals in the soil, leading to soil acidification. This can reduce the pH of the soil, making it more acidic and harmful to plant growth. Acidic soil can also cause toxic metals such as aluminum, lead, and mercury to be released into the soil, further damaging its quality.
Land degradation caused by sulfuric acid can lead to reduced biodiversity, as it can harm the growth of plants and reduce the availability of nutrients for other organisms. This can have negative impacts on the ecosystem, including the loss of habitat for wildlife and reduced soil fertility for agriculture.
.

.
To prevent land degradation from sulfuric acid, industries that use this chemical are required to have proper waste management systems in place. This includes treating the acid before it is disposed of and avoiding dumping it on the ground.
In addition, land remediation measures such as adding lime to the soil to neutralize the acid and adding organic matter to improve soil structure and fertility can be used to restore degraded land.
Overall, it is important to properly manage and dispose of waste sulfuric acid to prevent land degradation, protect biodiversity, and maintain healthy ecosystems.
.
Hazardous Materials
Sulfuric acid is a highly hazardous material that requires careful handling and disposal to avoid accidents that pose risks to human health and the environment.
It is highly corrosive and can cause severe chemical burns if it comes into contact with skin or eyes. Inhaling sulfuric acid vapors can cause respiratory problems and damage to the lungs.
Improper handling or disposal of sulfuric acid can lead to accidents such as spills, leaks, or releases into the environment. These accidents can have serious consequences, including:
.
- Health Risks: Sulfuric acid exposure can cause severe burns, respiratory problems, and other health issues. Accidents involving sulfuric acid can lead to injuries and illnesses among workers and members of the public.
- Environmental Damage: Sulfuric acid can contaminate soil and water, harming plants and animals and disrupting ecosystems. Accidents involving sulfuric acid can lead to environmental damage, including soil and water pollution, and harm to wildlife and aquatic life.
- Property Damage: Sulfuric acid is highly corrosive and can damage buildings, equipment, and infrastructure. Accidents involving sulfuric acid can lead to property damage and financial losses for businesses and individuals.
.
To prevent accidents involving sulfuric acid, industries that use this chemical are required to have proper handling and disposal systems in place.
.
This includes providing appropriate protective equipment and training for workers, as well as implementing emergency response plans in case of accidents. Sulfuric acid waste must be stored and transported in appropriate containers and disposed of at licensed facilities.
.
Overall, proper handling and disposal of sulfuric acid are essential to prevent accidents and protect human health and the environment.
