.

.
What Is Sulfur Coated Urea?
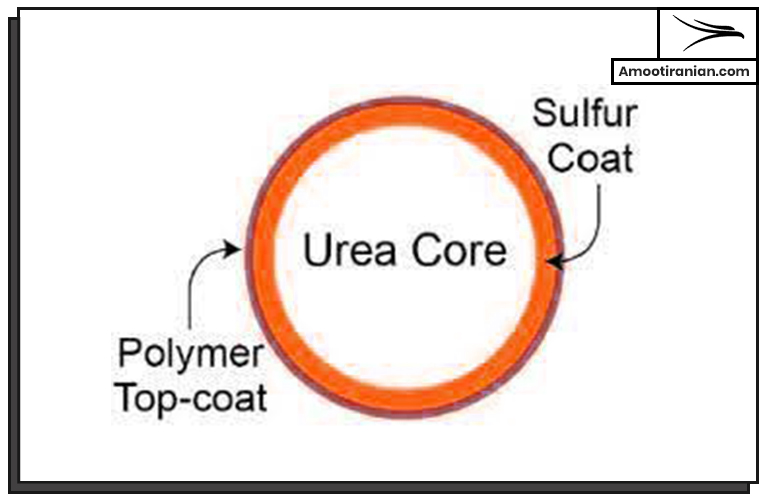
Sulfur-coated urea (SCU) is a type of slow-release nitrogen fertilizer. It is made by coating urea granules with a layer of sulfur. In this way the urea granules gradually breaks down over time and releases the nitrogen into the soil.
.
SCU is a slow and controlled release fertilizer.
.

.
The slow-release mechanism of SCU allows for a more efficient use of the nitrogen by the plants, reducing the risk of:
- leaching
- volatilization
- runoff
.
Additionally, the sulfur in the coating can provide some extra benefits to the soil, such as:
- improving soil pH
- enhancing nutrient availability
- reducing soil-borne diseases
.
SCU is commonly used in agricultural and horticultural applications, and it can be blended with other fertilizers or applied alone.
.
What Color Is Sulfur Coated Urea?
Sulfur-coated urea is typically yellow in color. The yellow color comes from the sulfur coating, which is added to the urea to control the release of nitrogen into the soil.
.
The sulfur coating helps to slow down the release of nitrogen and provide a more even and consistent supply of nutrients to plants over time.
.
What Is The Formula For Sulfur Coated Urea?
The formula for sulfur-coated urea is (NH2)2CO, which is urea, coated with a layer of sulfur.
.
The sulfur layer controls the release of urea into the soil, which makes it a slow-release nitrogen fertilizer.
.
The amount of sulfur coating can vary, typically ranging from 10 to 30 percent of the total weight of the product.
.
.
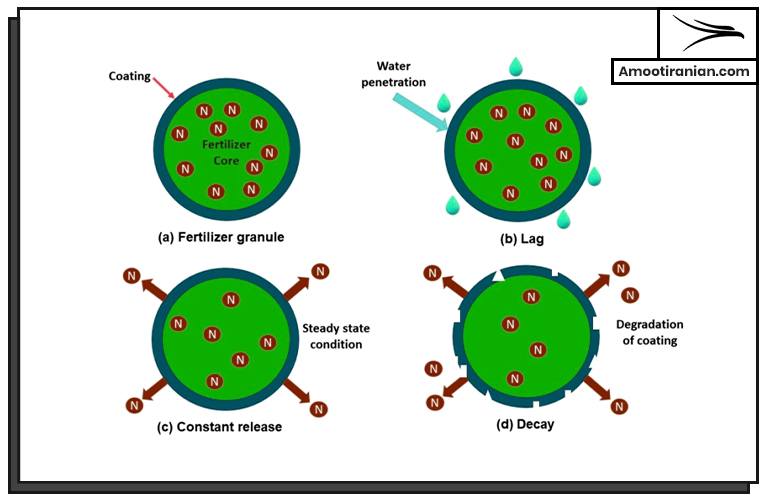
What Is The Purpose Of Coated Urea?
Coated urea is a type of fertilizer that is designed to slowly release nitrogen into the soil over a period of time. The purpose of using coated urea is: 1. to improve the efficiency of nitrogen uptake by crops 2. reduce nitrogen losses through leaching or volatilizatio
.
The coating on the urea granules is usually made of materials such as polymers or resins that are designed to control the release of nitrogen.
As the coated urea is applied to the soil, the coating slowly dissolves, releasing nitrogen at a controlled rate.
This slow-release mechanism helps to provide a steady supply of nitrogen to the crop over an extended period, which can result in better plant growth, higher yields, and improved nutrient use efficiency.
.
In addition to its role as a fertilizer, coated urea has other uses such as in the production of melamine, which is used in the manufacture of various products such as laminates, coatings, and adhesives.
.
.
How Does Sulfur Coated Urea Work?
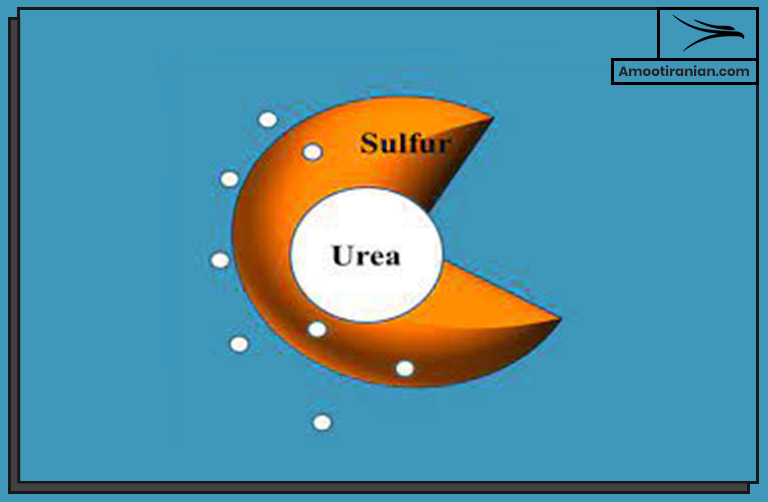
Sulfur-coated urea (SCU) is a type of controlled-release fertilizer that slowly releases nitrogen to plants over an extended period.
The coating on the urea granules is made up of elemental sulfur, which reacts with moisture in the soil to form a slow-release layer of ammonium sulfate around the urea granules.
.
When the SCU granules are applied to the soil, the sulfur coating gradually dissolves, allowing the nitrogen to be released slowly over several weeks to months.
This slow-release of nitrogen provides a consistent supply of nutrients to the plants, which helps to improve growth, increase yield, and reduce the risk of nutrient leaching.
.
What Are The Advantageous Of Sulfur Coated Urea?
.
| Advantage | Explanation |
| Controlled-release | SCU gradually releases nitrogen to plants over a lengthy period, providing a consistent and steady supply of nutrients. |
| Reduced nutrient loss | The slow-release nature of SCU reduces the danger of nutrient deficiency due to leaching or volatilization. It can save on fertilizer costs and reduce pollution. |
| Improved plant growth | The consistent supply of nutrients by sulfur coated urea can: 1. advance plant growth 2. increase yield 3. enhance crop quality. |
| Reduced fertilizer applications | Because SCU releases nutrients over a longer period, it may require fewer applications than traditional fertilizers. It decreases labor and fertilizer costs. |
| Reduced environmental impact | By dropping nutrient loss and pollution, sulfur coated urea can help to protect water quality and minimize ecological damages. |
.
Overall, sulfur-coated urea is an effective and environmentally friendly fertilizer option for agricultural and horticultural use.
.
.
Sulfur Coated Urea Disadvantages
| Disadvantage | Explanation |
| Higher cost | SCU is more expensive than traditional urea fertilizer. The cost of the sulfur layer and the process of making SCU is added. |
| Slow release rate | The slow-release nature of SCU may not be suitable for crops that require a fast nutrient uptake, such as: 1. those in the early stages of growth 2. those with a short growing season |
| Limited nutrient availability | SCU may not provide enough nitrogen during peak plant demand periods, It leads to: 1. lower crop yields 2. reduced crop quality |
| Sulfur buildup in soil | Overuse of SCU can lead to a buildup of elemental sulfur in the soil. It can lower soil pH and affect soil fertility. |
| Storage and handling challenges | The sulfur coating on SCU can make it more difficult to handle and store compared to traditional fertilizers. It may require special equipment for application. |
It’s worth noting that many of these potential disadvantages can be mitigated by careful selection, handling, and use of SCU, and that the benefits of this type of controlled-release fertilizer often outweigh the drawbacks.
