.

.
What Does NPK Mean In Fertilizer?
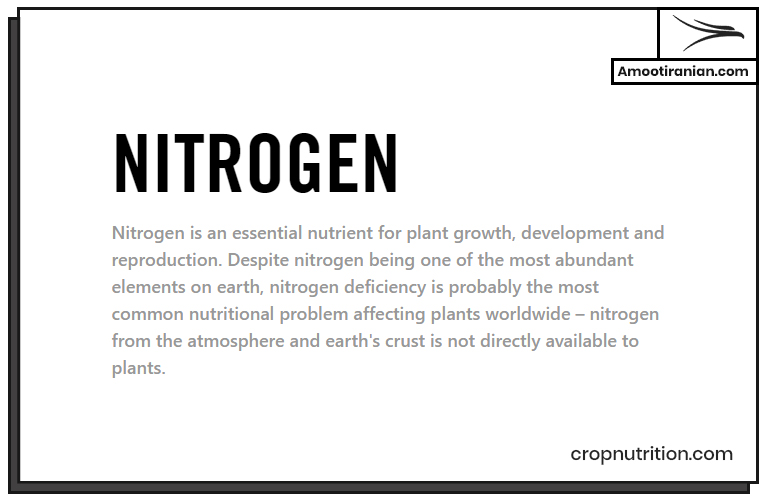
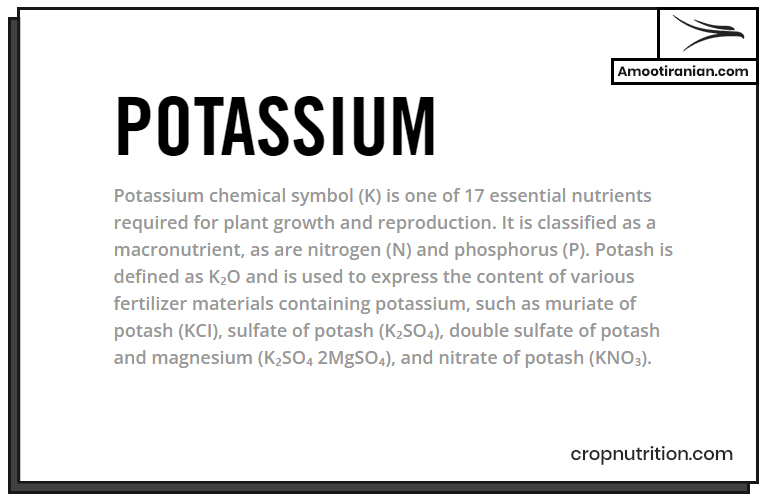
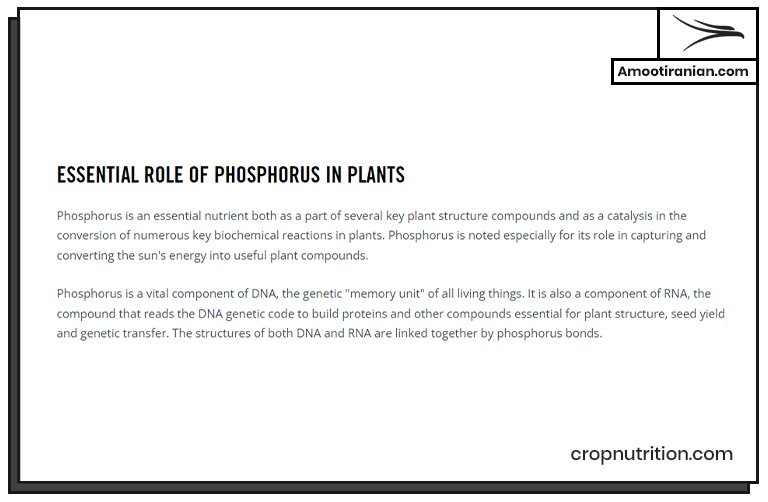
NPK stands for: 1. Nitrogen 2. Phosphorus 3. Potassium These are the three essential nutrients that plants need to grow. NPK fertilizer is a kind of fertilizer that contains varying amounts of these three nutrients.
.
.
The NPK ratio on a fertilizer label specifies the percentage of each nutrient in the fertilizer.
For example, a fertilizer with an NPK ratio of 10-10-10 contains 10% nitrogen, 10% phosphorus, and 10% potassium.
.
Different types of plants have different nutrient requirements, so it’s important to choose a fertilizer with the right NPK ratio for the plants you are growing.
.
.
N-P-K Fertilizer Formula
The formula for N-P-K fertilizer is based on the chemical symbols for the three essential nutrients that it contains:
- Nitrogen (N)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Potassium (K)
.
The NPK formula is expressed as a series of three numbers separated by dashes, representing the percentage by weight of each nutrient in the fertilizer.
.
For example, a fertilizer with an N-P-K ratio of 10-10-10 contains:
- 10% nitrogen
- 10% phosphorus
- 10% potassium
.
Similarly, a fertilizer with an N-P-K ratio of 20-10-5 contains:
- 20% nitrogen
- 10% phosphorus
- 5% potassium
.
It’s important to note that there are many different types of N-P-K fertilizers available, each with a different ratio of nutrients.
The best N-P-K ratio for your plants will depend on their specific needs and the soil conditions in your garden.
It’s a good idea to consult with a local gardening expert or conduct a soil test to determine the best fertilizer for your plants.
.

.
What Is NPK Fertilizer Examples?
| N-P-K Ratio | Fertilizer Type | Example |
| 10-10-10 | All-purpose fertilizer | Miracle-Gro All Purpose |
| 4-6-2 | Organic fertilizer | Espoma Garden Tone |
| 18-46-0 | High-phosphorus fertilizer | Superphosphate |
| 24-8-16 | Lawn fertilizer | Scotts Turf Builder |
| 15-30-15 | Flower and vegetable fertilizer | Jobe’s Organics |
.

.
As mentioned previously, It’s important to note that the best fertilizer for your plants will depend on their specific needs and the soil conditions in your garden.
.
How is NPK fertilizer manufactured?
.
1. What are the raw materials for NPK fertilizer?
The raw materials for NPK fertilizer are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These three essential nutrients are extracted from natural sources such as:
- Nitrogen: air, ammonia, and urea
- Phosphorus: rock phosphate, bone meal, and guano
- Potassium: potash deposits, seaweed, and wood ash
.
In addition to these primary sources, there are also secondary sources of these nutrients, such as animal manure, compost, and crop residues.
These materials can be processed and incorporated into NPK fertilizers to provide additional nutrients and improve soil quality.
It’s important to note that the source of these nutrients can vary depending on the manufacturer and the specific type of NPK fertilizer being produced. Some NPK fertilizers may also contain other trace elements or micronutrients to address specific nutrient deficiencies in soil.
.
2. NPK fertilizer manufacturing process
| Step | Description |
| A | Extraction of raw materials – Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium are extracted from natural sources such as rock phosphate, potash deposits, and air. |
| B | Separation and purification of raw materials – The extracted raw materials are purified and separated to remove impurities and increase the concentration of the desired nutrients. |
| C | Mixing of raw materials – The purified and concentrated raw materials are mixed in the appropriate ratios to produce the desired NPK ratio. |
| D | Granulation – The mixed raw materials are dried and then formed into granules using a granulation process. |
| E | Cooling – The granules are then cooled to room temperature. |
| F | Screening – The cooled granules are then screened to remove any oversized or undersized particles. |
| G | Coating – The screened granules may be coated with additional nutrients or protective coatings to enhance their performance or protect them from moisture or other environmental factors. |
| H | Packaging – The finished NPK fertilizer is then packaged into bags or other containers for distribution to retailers or end-users. |
It’s worth noting that there may be variations in the manufacturing process depending on the specific type of NPK fertilizer being produced and the manufacturer’s production methods.
.

.
What Is The Best NPK Fertilizer?
The best NPK fertilizer for your plants will depend on the specific needs of your plants and the soil conditions in your garden.
Different plants have different nutrient requirements, and the optimal NPK ratio can vary depending on factors such as:
- soil pH
- moisture levels
- nutrient availability
.
In general, an all-purpose fertilizer with a balanced NPK ratio such as 10-10-10 or 20-20-20 can be a good choice for many types of plants. These fertilizers provide equal amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which can help promote overall growth and development.
.
However, for plants with specific nutrient requirements, it may be necessary to use a fertilizer with a different NPK ratio.
For example, plants that require high levels of phosphorus, such as root vegetables or flowering plants, may benefit from a fertilizer with a higher phosphorus content, such as 15-30-15 or 10-20-10.
.
Before applying any fertilizer, it’s a good idea to consult with a local gardening expert or conduct a soil test to determine the best fertilizer for your plants.
The soil test will help determine the current nutrient levels in your soil and identify any deficiencies that need to be addressed.
Based on the soil test results, you can choose the best NPK fertilizer for your plants to help them grow healthy and strong.
.
What Is The Benefit Of NPK Fertilizer?
| Benefit | Description |
| Promotes growth | 1. Nitrogen is essential for the growth of leaves and stems. 2. Phosphorus helps with root development and flower formation. 3. Potassium promotes overall plant growth and stress tolerance. NPK fertilizers provide these essential nutrients in balanced ratios, helping to promote healthy growth and development. |
| Improves yield | NPK fertilizers can help improve crop yield by providing plants with the nutrients they need to grow and produce fruit or flowers. By addressing nutrient deficiencies in the soil, NPK fertilizers can also help to prevent plant diseases and pest infestations, which can lead to reduced yields. |
| Enhances color and flavor | NPK fertilizers can help enhance the color and flavor of fruits and vegetables by providing plants with the nutrients they need to develop vibrant colors and strong flavors. This is particularly important for crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and berries, which are prized for their taste and appearance. |
| Increases nutrient uptake | NPK fertilizers can help improve nutrient uptake by plants, making it easier for them to absorb essential nutrients from the soil. By providing a balanced mix of nutrients, NPK fertilizers can help prevent nutrient imbalances that can lead to stunted growth and poor yields. |
| Improves soil quality | NPK fertilizers can help improve soil quality by increasing the organic matter content and improving soil structure. This can help to promote healthy root growth and improve water retention in the soil, leading to healthier and more productive plants. |
.
Is NPK Good For All Plants?
While NPK fertilizer can be beneficial for many plants, it's not necessarily suitable for all types of plants or growing conditions. Different plants have different nutrient requirements, and the optimal NPK ratio can vary depending on factors such as: 1. soil pH 2. moisture levels 3. nutrient availability
.
In some cases, applying too much NPK fertilizer can lead to nutrient imbalances, which can harm plants and reduce their growth and productivity.
Overuse of nitrogen, in particular, can lead to excessive leaf growth at the expense of fruit or flower development, and can also make plants more susceptible to disease and pest infestations.
.
It’s important to take into account the specific needs of your plants and the soil conditions in your garden when selecting a fertilizer. Before applying any fertilizer, it’s a good idea to consult with a local gardening expert or conduct a soil test to determine the best fertilizer for your plants.
This will help you ensure that you are providing your plants with the nutrients they need without overfertilizing or causing nutrient imbalances.
.

.
When Should I Use NPK?
The timing for using NPK fertilizer will depend on the specific needs of your plants and the soil conditions in your garden.
.
In general, it's a good idea to apply NPK fertilizer when your plants are actively growing and developing. This can help ensure that they have the nutrients they need to support healthy growth and productivity.
.
Here are some general guidelines for when to use NPK fertilizer:
Vegetables and annual flowers
For most vegetable and annual flower crops, it’s best to apply NPK fertilizer at planting time or shortly after planting. You can also apply a second application of fertilizer about halfway through the growing season to help support continued growth and productivity.
Perennial plants
For perennial plants such as shrubs, trees, and fruit bushes, it’s best to apply NPK fertilizer in the early spring before new growth begins. You can also apply a second application of fertilizer in the late spring or early summer to help support strong growth and fruit development.
Lawns
For lawns, it’s best to apply NPK fertilizer in the early spring when the grass is just starting to grow, and again in the fall to help support root growth and winter hardiness.
.
It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when applying NPK fertilizer to ensure that you are using the correct amount for your plants and soil conditions.
Overuse of fertilizer can cause nutrient imbalances and can damage your plants.
.
How Do You Mix NPK Fertilizer?
Mixing NPK fertilizer involves combining the three key nutrients – nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium – in the correct ratios to provide plants with the balanced nutrition they need to grow and thrive.
.
Here’s a general overview of how to mix NPK fertilizer:
Determine the NPK ratio
NPK fertilizers come in a range of ratios, such as 10-10-10, 5-10-5, or 15-5-10, which indicate the relative amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the fertilizer. Determine the appropriate NPK ratio for your plants by consulting a gardening expert or conducting a soil test.
Measure out the fertilizer
Once you have determined the appropriate NPK ratio, measure out the correct amount of fertilizer based on the instructions on the fertilizer label or package. Use a scale or measuring cup to ensure accurate measurement.
Mix the fertilizer
Combine the measured fertilizer with a carrier material, such as sand, sawdust, or perlite, to help distribute the fertilizer evenly and prevent clumping. Use a bucket or mixing container to thoroughly blend the fertilizer and carrier material.
Apply the fertilizer
Apply the mixed fertilizer to your plants according to the manufacturer’s instructions or the guidelines provided by your gardening expert. Apply the fertilizer evenly and avoid getting it on the foliage or stems of your plants, as this can burn the plant tissue.
Water the plants
After applying the fertilizer, water your plants thoroughly to help distribute the nutrients throughout the soil and encourage uptake by the plant roots.
.
It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when mixing and applying NPK fertilizer to ensure that you are using the correct amount and ratio for your plants and soil conditions.
Overuse of fertilizer can harm your plants and lead to nutrient imbalances, so it’s important to use fertilizers judiciously and as directed.
.
What Happens If You Use Too Much NPK?
| Consequence | Description |
| Nutrient imbalances | Excessive use of NPK fertilizer can upset the balance of nutrients in the soil, leading to deficiencies or excesses of certain nutrients. This can harm plants and reduce their growth and productivity. |
| Leaf burn | Overuse of nitrogen in particular can cause leaf burn, where the edges of leaves turn brown and crispy. This can harm the plant and reduce its ability to photosynthesize. |
| Reduced fruit or flower production | Overuse of nitrogen can also lead to excessive leaf growth at the expense of fruit or flower development. This can reduce the plant’s yield and productivity. |
| Environmental pollution | Excessive use of NPK fertilizer can lead to runoff of excess nutrients into nearby water sources, causing pollution and potential harm to aquatic ecosystems. |
| Increased pest and disease susceptibility | Overuse of nitrogen can make plants more susceptible to certain pests and diseases, as well as weaken their overall health and resilience. |
| Reduced soil quality | Excessive use of NPK fertilizer can lead to degradation of soil structure and quality over time, reducing its ability to support healthy plant growth. |
.

.
Is NPK Fertilizer Safe?
NPK fertilizer is safe to use if used according to the manufacturer’s instructions or guidelines from gardening experts.
However, like any chemical product, NPK fertilizer can pose risks if not handled and used properly. Here are some important safety considerations when using NPK fertilizer:
Wear protective gear
When handling NPK fertilizer, wear gloves, long sleeves, and pants to avoid skin contact. Wear goggles or other eye protection to prevent eye irritation or injury.
Store properly
Store NPK fertilizer in a cool, dry, and secure location out of reach of children and pets. Keep fertilizer bags or containers tightly sealed to prevent moisture or other contaminants from entering.
Use as directed
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mixing and applying NPK fertilizer. Overuse or misuse of fertilizer can harm plants and the environment, and may also pose health risks to humans or animals.
Use caution around water sources
Do not apply NPK fertilizer near water sources or in areas where it may leach into groundwater. This can cause pollution and potential harm to aquatic ecosystems.
Dispose of properly
Dispose of unused or expired NPK fertilizer according to local regulations or guidelines. Do not dump fertilizer in trash or down the drain.
.
Overall, NPK fertilizer is safe to use if handled and used properly.
Be sure to follow all safety precautions and guidelines to minimize any potential risks to yourself, your plants, and the environment.
.
What Is NPK 20 20 20 Used For?
NPK 20 20 20 is a type of fertilizer that contains a balanced mix of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in equal proportions.
This fertilizer is commonly used in agriculture, horticulture, and gardening to provide a balanced nutrient supply to plants.
The nitrogen in NPK 20 20 20 helps plants to grow foliage, stems, and leaves, which is important for photosynthesis and overall plant growth.
The phosphorus in the fertilizer is essential for root development and fruit and flower production, while potassium helps to improve the plant’s resistance to stress, disease, and environmental factors.
.
NPK 20 20 20 is often used for crops that require high levels of nutrients, such as vegetables, fruits, and flowers.
It is also commonly used for lawns and landscaping, as well as in hydroponic systems.
However, it’s important to note that the appropriate type and amount of fertilizer will vary depending on the specific plant species and growing conditions, so it’s always best to consult with a professional or refer to the fertilizer’s instructions before use.
.
What Is 30 10 10 Fertilizer Good For?
30 10 10 fertilizer is a type of nitrogen-rich fertilizer that contains 30% nitrogen (N), 10% phosphorus (P), and 10% potassium (K).
This high nitrogen content makes it an ideal fertilizer for promoting vegetative growth in plants, particularly during the early stages of growth.
The nitrogen in 30 10 10 fertilizer helps plants to develop strong stems and lush foliage, which is essential for photosynthesis and overall plant health.
Additionally, the phosphorus and potassium in the fertilizer provide the necessary nutrients for root development and overall plant vigor.
.
This type of fertilizer is often used for lawn care, as it helps to promote green and healthy grass growth.
It is also commonly used for plants that require high levels of nitrogen, such as corn, wheat, and other grains. However, it’s important to use the appropriate type and amount of fertilizer for specific plants and growing conditions, as excessive use of nitrogen can lead to overgrowth, decreased fruit or flower production, and can also negatively impact the environment.
.
What Is 15 15 30 Fertilizer Used For?
The 15-15-30 fertilizer is formulated to provide balanced nutrition to plants with moderate to high potassium needs.
The high potassium content in this fertilizer makes it ideal for plants in the flowering or fruiting stage of growth. It can also be used to correct potassium deficiency in the soil or to promote root development.
This type of fertilizer is commonly used in greenhouse and nursery operations to improve plant quality and yield.
.
What Is 7 20 30 Fertilizer Good For?
The high potassium content of 7-20-30 fertilizer is especially beneficial for plants that require a lot of potassium, such as tomatoes, peppers, and other fruiting vegetables. Additionally, the higher phosphorus content can help stimulate root growth and improve plant vigor.
A fertilizer with an NPK ratio of 7-20-30 is high in phosphorus and potassium and relatively low in nitrogen.
.
This type of fertilizer is often recommended for use on flowering plants, fruits, and vegetables during the blooming and fruiting stages of growth.
.
The high levels of phosphorus and potassium promote strong root development, healthy flowering, and fruit development, while the lower nitrogen content helps to prevent excessive vegetative growth that can hinder flower and fruit production.
It can also be used to help correct soil deficiencies in phosphorus and potassium.
