.
.
How Is Urea Produced from Natural Gas?
How is urea produced step by step? Which gas is used for urea production? What is the raw material for urea production?
.
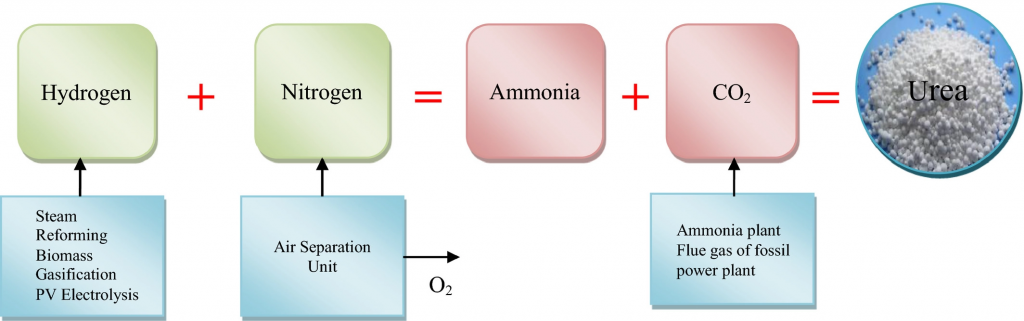
Urea is primarily produced from natural gas using the Haber-Bosch process, which involves three main steps.
.
Firstly, natural gas undergoes steam reforming, which involves heating it to high temperatures in the presence of steam and a catalyst, typically nickel. This process converts the methane in natural gas into synthesis gas, a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
.
Secondly, the synthesis gas is then reacted with nitrogen from the air to produce ammonia in a process called the Haber process. This process takes place at high pressures (100-250 atm) and temperatures (400-550°C), and requires a catalyst, typically iron or ruthenium.
.
Finally, the ammonia is reacted with carbon dioxide in a process called the urea synthesis reaction, which takes place at high pressures (150-300 atm) and temperatures (150-250°C). This reaction produces urea and water, which are then separated and purified.
.
.
The overall process is:
- highly energy-intensive
- requires large amounts of natural gas
- needs significant amounts of electricity to power the process
However, the resulting urea is a valuable commodity widely used in agriculture as a fertilizer, and also has industrial applications such as in the production of plastics and resins.
.
The urea production process from natural gas involves several additional steps to ensure the purity and quality of the final product.
After the urea is synthesized, it is typically in the form of a highly concentrated aqueous solution, which must be purified and concentrated further.
The urea solution is first sent to a vacuum evaporation unit, where water is removed and the urea is concentrated to around 99% purity.
The concentrated urea solution is then sent to a prilling tower, where it is sprayed into a hot, dry air stream to form small droplets, which then solidify into small spheres called prills.
The prills are then cooled and screened to ensure uniform size and shape, and are then stored for shipping and distribution.
..
Overall, the production of urea from natural gas is a complex and energy-intensive process, but one that is essential for meeting the global demand for fertilizer and other industrial applications.
The use of natural gas as a feedstock for urea production has several advantages, including the abundance of natural gas reserves and the relatively low cost compared to other feedstocks such as coal or oil.
.
.
Urea is now prepared commercially in vast amounts from liquid ammonia and liquid carbon dioxide. These two materials are combined under high pressures and elevated temperatures to form ammonium carbamate, which then decomposes at much lower pressures to yield urea and water.
.
How Much Natural Gas Is Required to Produce 1 Ton of Urea?
It takes between 20 MMBtu and 22 MMBtu (million British thermal units) of natural gas to produce one ton of urea.
This includes the natural gas required to produce the ammonia feedstock, which itself requires 0.57 tons of ammonia and 3.0 MMBtu to 3.5 MMBtu of natural gas per ton of urea.
The exact amount of natural gas required may vary depending on the specific production process and efficiency of the plant.
.
Is Urea 100% Nitrogen?
No, urea is not 100% nitrogen.
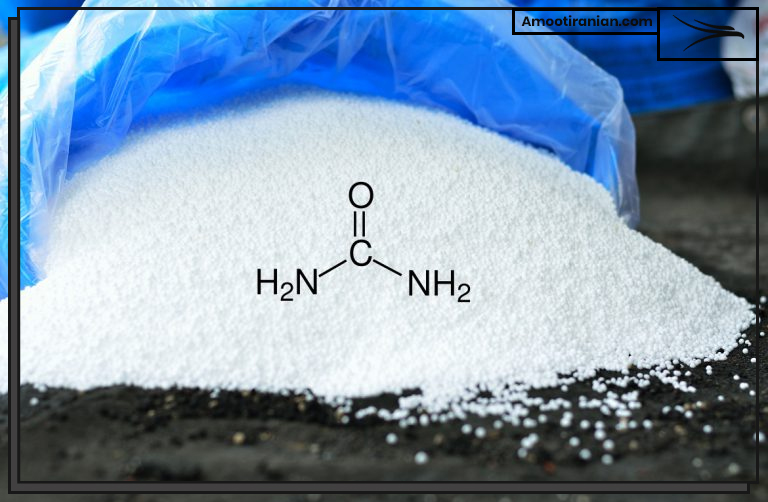
Urea is a compound that contains nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
The chemical formula for urea is (NH2)2CO, which means that it contains two nitrogen atoms, four hydrogen atoms, and one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. The percentage of nitrogen in urea by weight is approximately 46%, which is the highest among common nitrogen fertilizers.
.

.
What Percentage of Urea Is Hydrogen?
.
6.72%
.
The chemical formula for urea is (NH2)2CO, which means that it contains:
- two nitrogen atoms
- four hydrogen atoms
- one carbon atom
- one oxygen atom
.
Therefore, the percentage of urea that is hydrogen by mass can be calculated as follows:
Mass of hydrogen in urea = 4 x molar mass of hydrogen
= 4 x 1.008 g/mol
= 4.032 g/mol
.
Molar mass of urea = (2 x molar mass of nitrogen) + (2 x molar mass of hydrogen) + molar mass of carbon + (2 x molar mass of oxygen)
= (2 x 14.007 g/mol) + (2 x 1.008 g/mol) + 12.011 g/mol + (2 x 15.999 g/mol)
= 60.055 g/mol
.
Therefore, the percentage of urea that is hydrogen by mass is:
(4.032 g/mol / 60.055 g/mol) x 100% = 6.72%
.
So the percentage of hydrogen in urea is approximately 6.72%
.
.

.
What Other Fertilizers Are Produced from Natural Gas?
Natural gas is used as a feedstock to produce several other fertilizers besides urea. Some of these fertilizers include:
| Fertilizer | Chemical Formula | Production Process |
| Ammonia | NH3 | Natural gas is reacted with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide, which are then reacted with nitrogen from the air to produce ammonia. |
| Urea | (NH2)2CO | Natural gas is first converted to synthesis gas, which is then reacted with carbon dioxide to produce ammonia. The ammonia is then reacted with carbon dioxide to produce urea. |
| UAN (urea ammonium nitrate) | varies | UAN is a liquid fertilizer that is made by mixing urea, ammonium nitrate, and water. The urea and ammonium nitrate can be produced from natural gas using the processes described above. |
| Methanol | CH3OH | Natural gas is reformed with steam to produce synthesis gas, which is then converted to methanol using a catalyst. Methanol can be used as a feedstock for the production of other fertilizers, such as formaldehyde and urea-formaldehyde. |
| Elemental sulfur | S | Elemental sulfur can be produced from natural gas by a process known as the Claus process, which involves burning natural gas to produce sulfur dioxide, which is then reacted with hydrogen sulfide to produce elemental sulfur. Elemental sulfur can be used as a direct fertilizer or further processed to produce sulfuric acid, which can be used to produce ammonium sulfate. |
.
Note that there are other fertilizers that can also be produced from natural gas, and the production processes may vary depending on the specific fertilizer and plant.
.
Enhance Your Crop Yield with Amoot’s High-Grade Urea & Sulfur Fertilizers
Amoot Iranian Trading Company is an old and experienced supplier and exporter of urea and sulfur fertilizers of Iran and Turkmenistan to many countries including Arabic, Asian, and African countries at best prices and the highest quality.
All steps of fertilizer export can be managed by Amoot professional team of experts from the beginning to the end.
.

.
Due to the strong relationship of Amoot Company with various reliable shipping companies of Iran like The Islamic Republic of Iran Shipping Line Group (IRSIL), fertilizer transportation in bulk or in containers is handled easily and professionally by Amoot’s team.
Amoot’s stocks are filled with fertilizers and your cargo will be delivered on time! Call us!
