This page is a complete investigation on sulfur chemical including sulfur definition, element, symbol, uses, and facts from A to Z.
Comprehensive data that can be used as your reliable reference anywhere you like.
.

.
History
What is sulfur?
Sulfur or Sulphur (symbol: S) is a chemical element with the atomic number 16.
It is a nonmetal that appears as a yellow crystalline solid at room temperature and is abundant in nature. Sulfur is an essential element for life and is found in many important biomolecules such as proteins and vitamins.
.
.
Sulfur has a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. It is used in the production of sulfuric acid, which is one of the most important industrial chemicals, and is also used in the manufacture of fertilizers, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
Sulfur is a key component in the production of rubber, and is also used in the vulcanization process, which gives rubber its strength and durability.
Sulfur is found in many minerals and ores, such as gypsum, Epsom salt, and pyrite. It is also found in natural gas and crude oil, and is often a byproduct of the refining process.
Sulfur can also be produced by various industrial processes, such as the Claus process, which recovers sulfur from hydrogen sulfide gas.
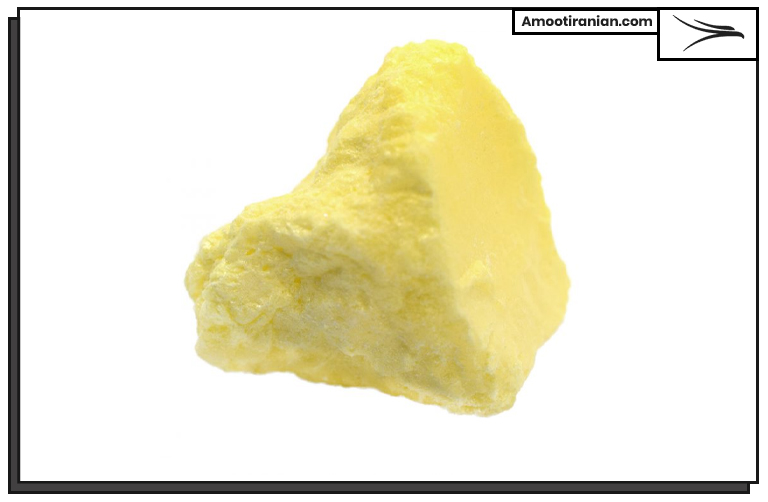

Sulfur History Facts
Sulfur has been known and used by humans since ancient times. The earliest recorded use of sulfur dates back to ancient China, where it was used in medicine and in the production of gunpowder.
In ancient Greece, sulfur was used as a fumigant to disinfect homes and as a medicine to treat a variety of ailments. The Roman naturalist Pliny the Elder described the use of sulfur as a disinfectant and for bleaching cloth.
During the Middle Ages, sulfur was widely used in the production of black powder for use in warfare. In the 16th century, the German alchemist Johann Becher discovered that sulfur could be combined with saltpeter (potassium nitrate) and charcoal to make a new kind of explosive powder that was more powerful than black powder.
This led to the development of gunpowder-based weapons that revolutionized warfare.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the production of sulfuric acid became a major industry, and sulfur was used in the manufacture of many other chemicals, such as fertilizers, dyes, and rubber.
In the 20th century, sulfur continued to be an important industrial chemical, but concerns about sulfur pollution led to the development of new technologies for reducing sulfur emissions from power plants and other industrial sources.
Today, sulfur is still used in a wide variety of applications, including the production of sulfuric acid, fertilizers, and rubber. It is also used as a fungicide and pesticide in agriculture, and as a component in some medications.
Sulfur is also an important element in the study of geology and the Earth’s history. Sulfur isotopes are used by scientists to study the origin of rocks and minerals, and to understand the evolution of the Earth’s atmosphere and the emergence of life on the planet.
In recent years, sulfur has also gained attention as a potential energy storage medium for renewable energy sources. Sulfur can be used in advanced battery technologies, such as lithium-sulfur batteries, which have the potential to store more energy than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Research in this area is ongoing, and there is hope that sulfur-based batteries could help to overcome some of the limitations of current energy storage technologies.
Sulfur is also an important component of many environmental processes. Sulfur cycles through the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and land, and plays a crucial role in regulating the planet’s climate.
Sulfur dioxide, a byproduct of fossil fuel combustion, can cause acid rain and other forms of pollution, which can have significant environmental and health impacts. Understanding the sulfur cycle and the ways in which human activities are affecting it is an important area of research.
Overall, sulfur has played a vital role in human history and continues to be an important element in many aspects of modern life.
As our understanding of this element continues to evolve, we are likely to find new and innovative uses for sulfur in a wide range of applications, from energy storage to environmental remediation.
.
Natural Occurrence and Distribution
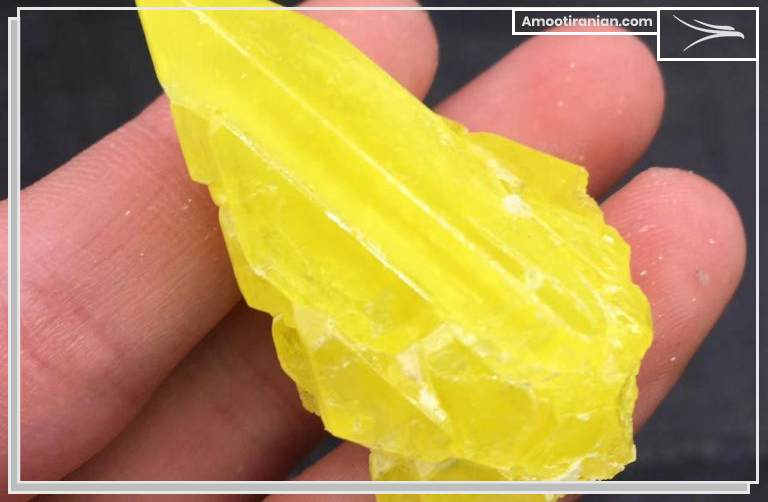
Sulfur is a naturally occurring element that is widely distributed throughout the Earth’s crust, oceans, and atmosphere. It is the 10th most abundant element in the universe, and the fifth most abundant element on Earth by mass.
Sulfur is found in many minerals, including sulfates, sulfides, and elemental sulfur. The most common sulfate mineral is gypsum (calcium sulfate), which is often used in construction materials.
.

.
The most common sulfide minerals are pyrite (iron sulfide), galena (lead sulfide), and sphalerite (zinc sulfide), all of which are important sources of metals.
Elemental sulfur occurs in many volcanic deposits, and is also found in large underground deposits in countries such as the United States, Russia, and Canada.
Sulfur is also present in natural gas and crude oil, where it can be found in the form of hydrogen sulfide and other sulfur-containing compounds. During the refining process, these compounds are typically removed and processed to produce sulfur as a byproduct.
In the Earth’s atmosphere, sulfur is present in the form of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and other sulfur-containing gases, which are produced by volcanic activity, forest fires, and human activities such as fossil fuel combustion.
Sulfur dioxide can react with water vapor and other chemicals in the atmosphere to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which can contribute to acid rain and other forms of pollution.
The distribution of sulfur varies widely depending on local geology and environmental conditions. Some areas have high concentrations of sulfur, while others have very low levels.
Understanding the natural occurrence and distribution of sulfur is important for a wide range of scientific and industrial applications, from mining and oil production to environmental monitoring and remediation.
.
Allotropy
Sulfur is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is a nonmetal and can exist in several different allotropes, which are different forms of the same element with different physical and chemical properties.
The most common allotrope of sulfur is the yellow, brittle, crystalline solid known as orthorhombic sulfur, or alpha-sulfur. This is the form of sulfur that is most commonly seen in nature and used in industry. It is stable at room temperature and pressure.
Another allotrope of sulfur is the monoclinic sulfur, or beta-sulfur, which is a powdery, yellow solid. It is less stable than alpha-sulfur and will gradually transform into it at room temperature.
Sulfur also has several other less common allotropes, including rhombic sulfur, which is a red crystalline solid, and plastic sulfur, which is a translucent, elastic material.
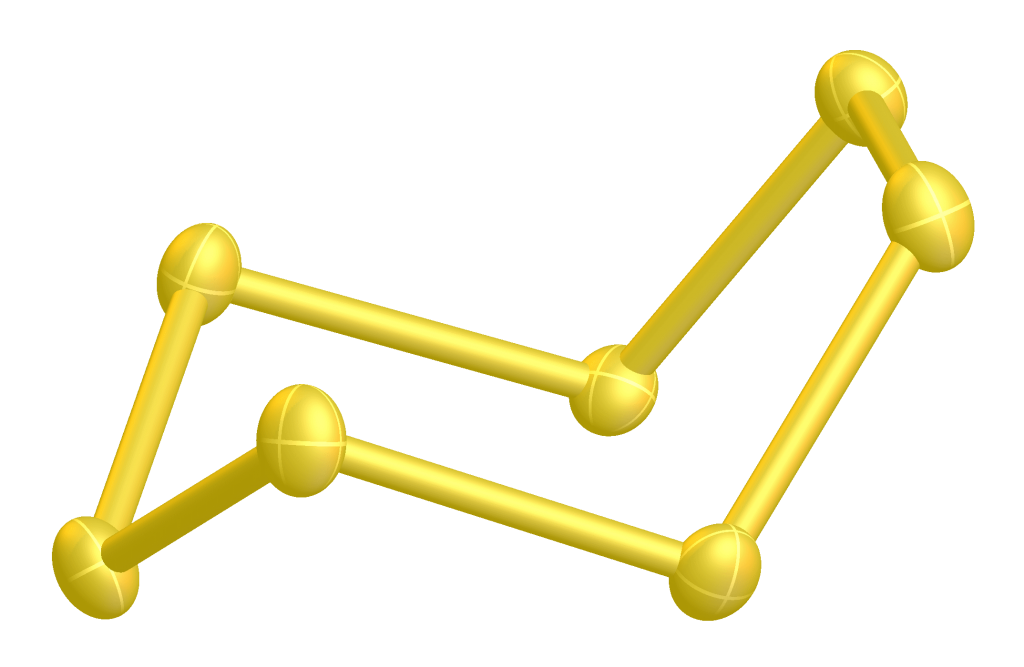
There is also a cyclo-octasulfur ring, which is an allotrope of sulfur that consists of eight sulfur atoms arranged in a ring.
The properties of these allotropes vary widely, including differences in color, density, melting point, and reactivity. These differences make sulfur useful for a variety of applications in industry and research.
Sulfur’s allotropes have different molecular structures and physical properties. For example, the monoclinic form of sulfur has a needle-like shape, while the orthorhombic form has a rhombic structure.
The rhombic sulfur allotrope has a reddish color and is less stable than the orthorhombic sulfur. This allotrope can be formed by crystallizing molten sulfur, and it has a lower melting point than the orthorhombic sulfur.
Plastic sulfur, on the other hand, is a unique allotrope of sulfur that has rubber-like properties.
It is formed by heating sulfur to a temperature of around 160 °C, at which point it becomes a soft, pliable material. Plastic sulfur can be molded into different shapes and is used in the manufacture of items like electrical insulators and adhesives.
Sulfur’s allotropes also have varying chemical reactivity. For example, orthorhombic sulfur is relatively unreactive at room temperature, but it can react with metals and other substances at higher temperatures.
Rhombic sulfur is more reactive than orthorhombic sulfur and can undergo chemical reactions with other elements and compounds.
Overall, the different allotropes of sulfur have a wide range of applications, including use in fertilizers, rubber, and matches. The unique physical and chemical properties of each allotrope make it useful in various industrial and research settings.
.
Commercial Production
Sulfur is commercially produced from both natural and synthetic sources. The majority of sulfur is produced from natural sources, primarily through the refining of petroleum and natural gas, and from the processing of ores containing sulfur.
Petroleum and natural gas contain sulfur compounds such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and mercaptans. When these compounds are removed from the oil or gas during refining, they are converted into elemental sulfur through a process known as Claus process.
.

.
The Claus process involves several steps, including the conversion of H2S to sulfur dioxide (SO2) and then the reaction of SO2 with more H2S to form elemental sulfur.
Sulfur can also be produced through the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal or oil, which contain sulfur compounds. During combustion, these compounds are converted into sulfur dioxide, which can then be processed into sulfur through the Claus process or other methods.
In addition to natural sources, sulfur can also be produced synthetically through the reaction of elemental sulfur with other chemicals.
For example, sulfuric acid, one of the most widely used industrial chemicals, can be produced by reacting sulfur trioxide (SO3) with water.
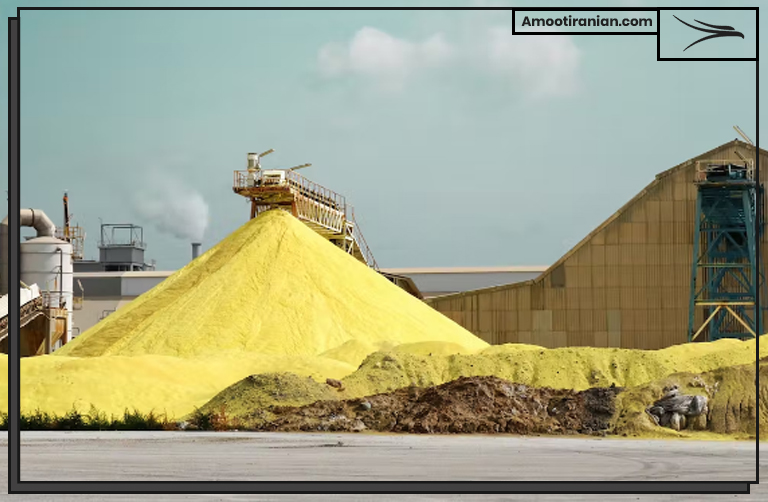
The production of sulfur from natural sources is the most common method and accounts for the majority of the world’s sulfur production.
The largest producers of sulfur include the United States, Russia, and China. Sulfur is used in a wide range of applications, including the production of fertilizers, rubber, and sulfuric acid, as well as in the petroleum and chemical industries.
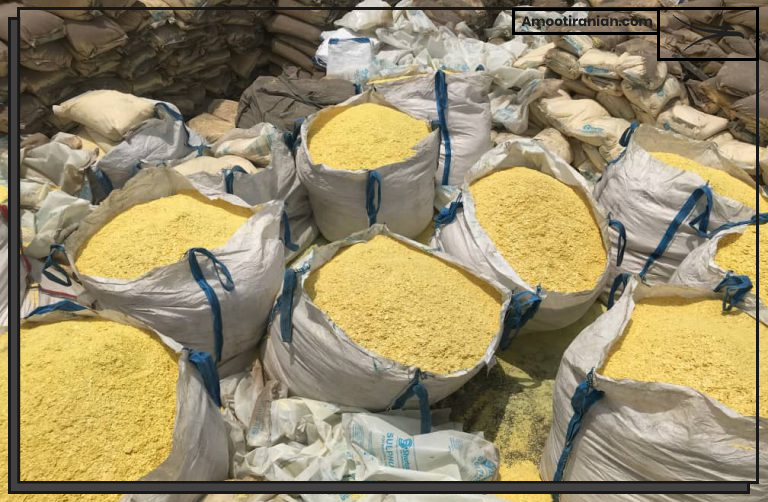
Once sulfur has been produced, it can be further processed and purified for use in different applications. Sulfur is typically melted and then purified through a distillation process to remove impurities and separate different grades of sulfur. The resulting sulfur can then be processed into different forms, including flakes, prills, and powder.
.

.
Sulfur is widely used in the production of fertilizers, particularly in the form of sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is used to convert phosphate rock into phosphoric acid, which is then used to make fertilizers.
Sulfur is also used in the production of other chemicals, including sulfites, which are used in the food and beverage industry as preservatives.
In addition to its use in the chemical industry, sulfur is used in a wide range of other applications.
For example, it is used in the production of rubber, where it acts as a vulcanizing agent. Sulfur is also used in the petroleum industry, where it is added to crude oil to remove impurities and improve its quality.
Another major use of sulfur is in the production of matches. The striking surface of a match contains sulfur, which reacts with potassium chlorate to produce heat and ignite the match head.
Overall, sulfur is a versatile element with a wide range of applications. Its commercial production from natural and synthetic sources is essential for meeting the demand for sulfur in various industries, and ongoing research and development is focused on finding new uses and applications for this important element.
.

.
Uses of Sulfur
Sulfur is a chemical element with the symbol “S” and atomic number 16. It is abundant and widely used in many industries. Here is a list of uses of sulfur:
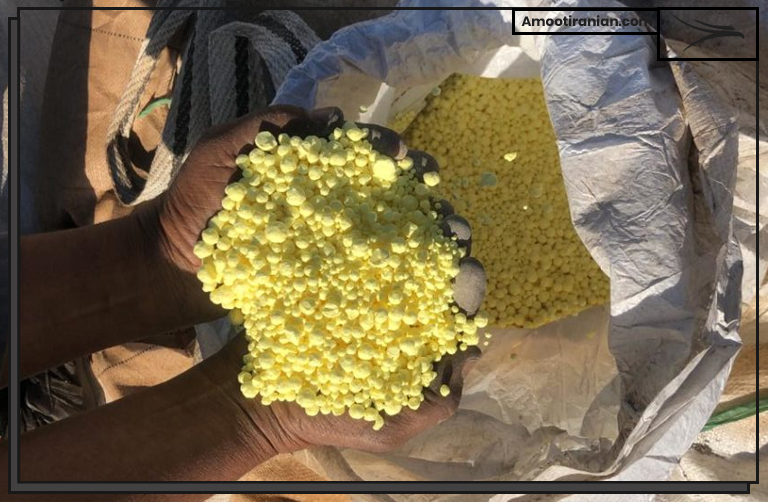
1_Fertilizers
Sulfur is used as a nutrient in fertilizers to help plants grow. It is often combined with other elements such as nitrogen and potassium to make complete fertilizers.
Sulfur is vital for plants’ growth, nitrogen metabolism, enzyme function, and protein synthesis.
.

.
What happens when a plant has too little sulfur? If plants do not receive enough sulfur, the following symptoms will be seen:
- growth reduction
- short stems
- reduced leaf size
- narrow leaves
- pale leaves
- yellowish-green or yellow leaves
- tips of leaves become necrotic
- red margins of young leaves
2_Sulfur coated urea
Sulfur Coated Urea (SCU) is also another useful and beneficial type of using sulfur in which urea fertilizer is covered with a layer of sulfur. In this way the sulfur repels water and do not allow urea to be dissolved fast in the water.
.
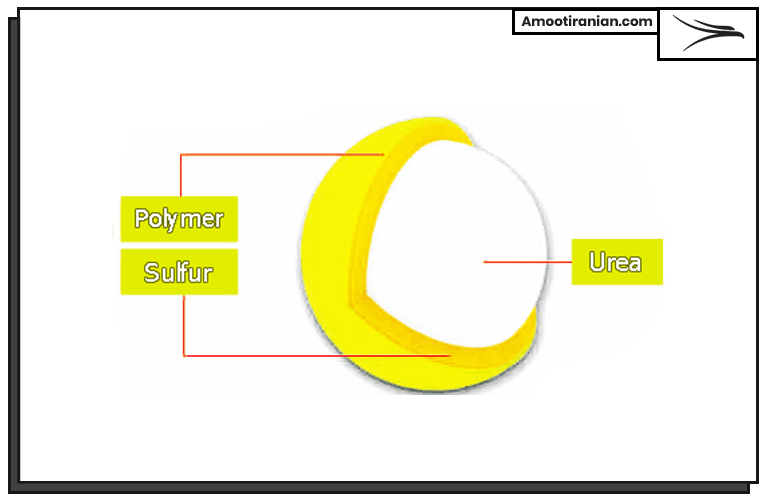
It is an economical slow-release fertilizer, does not allow urea chemical to be wasted.
.
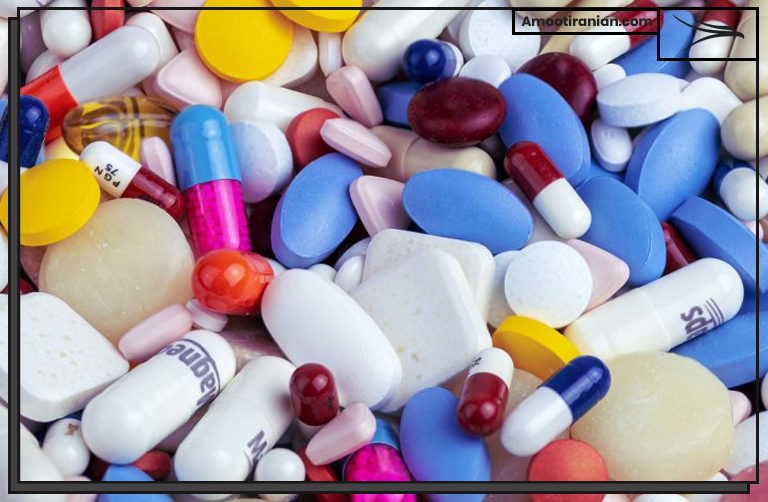
3_Pharmaceuticals
Sulfur compounds are used in the production of many medications, including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antifungal agents.
For instance, using sulfur in skin preparations for the cure of acne is common.
.

.
Some of the most commonly used sulfur-containing drugs include:
- Antibiotics: Sulfur-containing antibiotics, such as sulfonamides, are used to treat bacterial infections. These drugs work by inhibiting the growth and replication of bacteria. Sulfonamides have been used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, ear infections, and pneumonia.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen contain sulfur in their chemical structure. These drugs are used to reduce inflammation, pain, and fever. Sulfur-containing NSAIDs work by inhibiting the activity of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are responsible for the production of inflammatory mediators.
- Antifungal agents: Sulfur-containing antifungal agents, such as terbinafine and ketoconazole, are used to treat fungal infections. These drugs work by inhibiting the growth and replication of fungi. Sulfur-containing antifungals are used to treat a variety of fungal infections, including ringworm, athlete’s foot, and nail infections.
- Anticancer drugs: Sulfur-containing compounds, such as cisplatin and carboplatin, are used in chemotherapy to treat various types of cancer. These drugs work by interfering with the DNA replication process in cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and multiplying.
In addition to these drugs, sulfur-containing compounds are also used in the production of other medications, including drugs used to treat epilepsy, hypertension, and heart disease.
Overall, sulfur-containing drugs have played a significant role in the development of modern medicine, and they continue to be an important tool in the fight against various diseases and conditions.
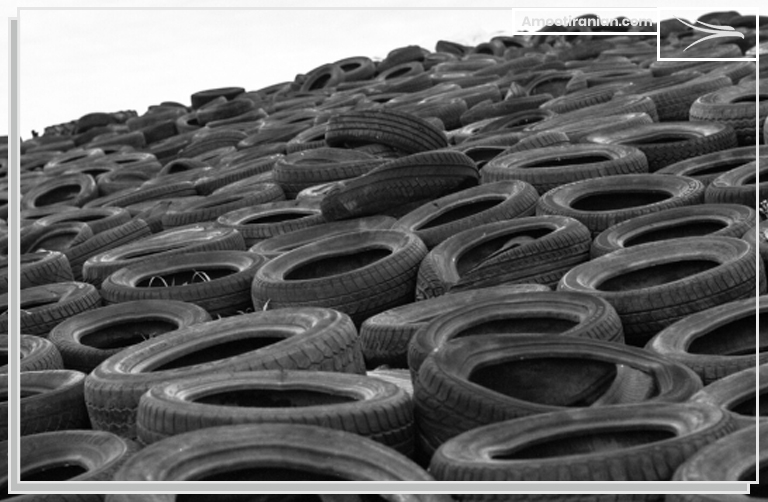
4_Rubber
Sulfur is a key component in the vulcanization of rubber. Vulcanization involves heating natural rubber with sulfur to make it stronger, more elastic, and resistant to abrasion.
Sulfur is a crucial component in the rubber industry, where it is used in the process of vulcanization to improve the strength, elasticity, and durability of natural and synthetic rubber materials.
Vulcanization is a process that involves heating rubber with sulfur, which causes chemical cross-linking between the rubber molecules, resulting in a stronger and more stable material.
.

.
During vulcanization, sulfur forms bridges between the rubber chains, creating a three-dimensional network that makes the rubber more elastic and resistant to abrasion, heat, and other environmental factors.
The amount of sulfur used in vulcanization can vary depending on the desired properties of the rubber product. For example, higher amounts of sulfur can result in a harder and more rigid material, while lower amounts can result in a softer and more flexible material.
5_Petroleum industry
Sulfur is often found in crude oil and natural gas. It must be removed from these products before they can be used as fuels. Sulfur is also used to make gasoline and diesel fuel burn cleaner, by reducing the amount of sulfur dioxide that is released into the air.
Sulfur is a naturally occurring element that is present in many crude oils and natural gas deposits. In the petroleum industry, sulfur is typically removed from crude oil and natural gas to meet environmental regulations and improve the quality of the final products.
.

.
Sulfur removal from crude oil is typically done by a process called hydrodesulfurization (HDS), which involves reacting the sulfur compounds in the crude oil with hydrogen gas over a catalyst at high temperature and pressure.
This process converts the sulfur compounds into hydrogen sulfide gas, which can be removed from the crude oil.
The hydrogen sulfide is then typically converted to elemental sulfur through a process called Claus process, which is widely used in the petroleum industry.
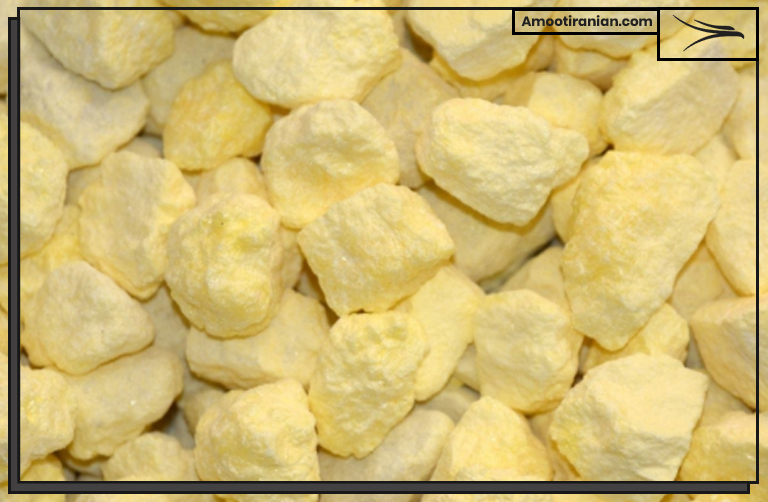
6_Food industry
Sulfur dioxide is often used as a preservative in dried fruits, fruit juices, and wine. It helps prevent the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms that can spoil food.
Sulfur is widely used in the food industry as a preservative, antioxidant, and color retention agent. Its use in food helps to prevent spoilage, improve shelf life, and maintain the quality of various food products. Sulfur compounds are added to a wide range of food products, including dried fruits, wine, beer, meat products, and baked goods.
One of the most common forms of sulfur used in the food industry is sulfur dioxide, which is added to food as a preservative and antioxidant.
.

.
Sulfur dioxide is effective at preventing the growth of bacteria, yeast, and mold, which can cause spoilage and deterioration of food.
It is commonly used in the preservation of dried fruits, such as raisins and apricots, and in the production of wine and beer, where it helps to prevent the growth of unwanted bacteria and yeasts.
Sulfur-based compounds are also used as color retention agents in food products. They are added to prevent discoloration and maintain the natural color of various food products, such as potatoes, apples, and fruit juices.
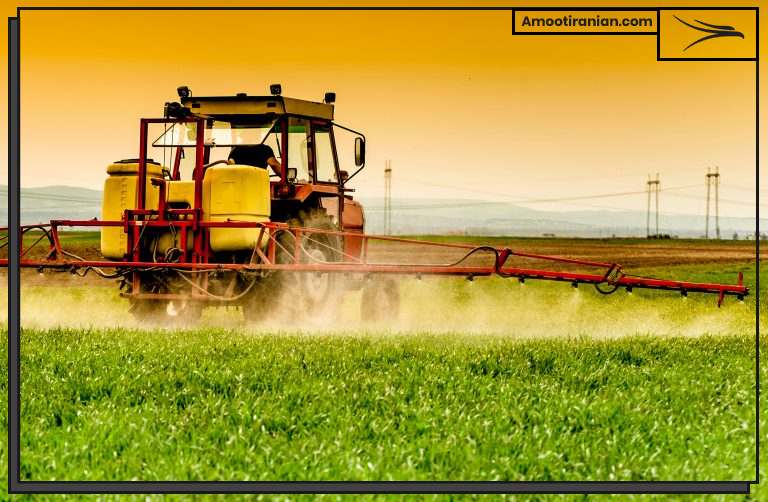
7_Pesticides
Sulfur-based compounds can also be used to bleach flour and sugar, giving them a whiter appearance.
Sulfur is an important component in many pesticides used to control pests in agriculture. It can also be used to control mites and other pests in home gardens.
Sulfur is used as an active ingredient in many pesticides, including fungicides and insecticides. Sulfur-based pesticides are used to control a wide range of pests, including mites, ticks, thrips, and various fungal diseases.
Sulfur-based fungicides work by inhibiting fungal growth and preventing the spores from germinating.
They are commonly used to control diseases in crops such as grapes, apples, strawberries, and citrus fruits. Sulfur-based fungicides are effective against a broad range of fungal pathogens, including powdery mildew, black spot, and rust.
.

.
They are relatively safe for humans and the environment and are commonly used in organic farming.
Sulfur-based insecticides, on the other hand, work by interfering with the respiratory system of insects, leading to their death. T
hey are effective against a wide range of insect pests, including mites, aphids, thrips, and whiteflies. Sulfur-based insecticides are commonly used in agricultural settings to control pests in crops such as grapes, tomatoes, and peppers.
They are also used in the control of pests in ornamental plants, such as roses and azaleas.
While sulfur-based pesticides are generally considered to be safe and effective, there are some potential drawbacks to their use. For example, sulfur can be phytotoxic at high concentrations, meaning it can damage plants if applied in excess.
Additionally, sulfur-based pesticides can be harmful to beneficial insects such as bees and ladybugs if not applied properly.
Therefore, it is important to follow the instructions on the pesticide label carefully and use sulfur-based pesticides only when necessary to minimize their impact on the environment.
8_Explosives
Sulfur is used in the production of gunpowder, matches, and fireworks. It is also a component in some types of explosives used in mining and construction.
Sulfur is commonly used both as an ingredient in explosive mixtures and as a separate component in the form of sulfuric acid.
The use of sulfur in explosives dates back to ancient times when it was used in gunpowder. Today, sulfur is still used in the production of a wide range of explosives, including dynamite, TNT, and ammonium sulfate explosives.
.

Sulfur plays several important roles in explosives. One of its key functions is to act as a fuel that provides energy when it reacts with an oxidizer, such as nitrate or chlorate. In addition to providing energy, sulfur also acts as a sensitizer that can lower the activation energy required for an explosive reaction to occur.
This can make the explosive more reactive and increase its power. Finally, sulfur can also act as a stabilizer that helps to prevent the explosive from degrading over time, ensuring that it remains safe and effective for longer periods.
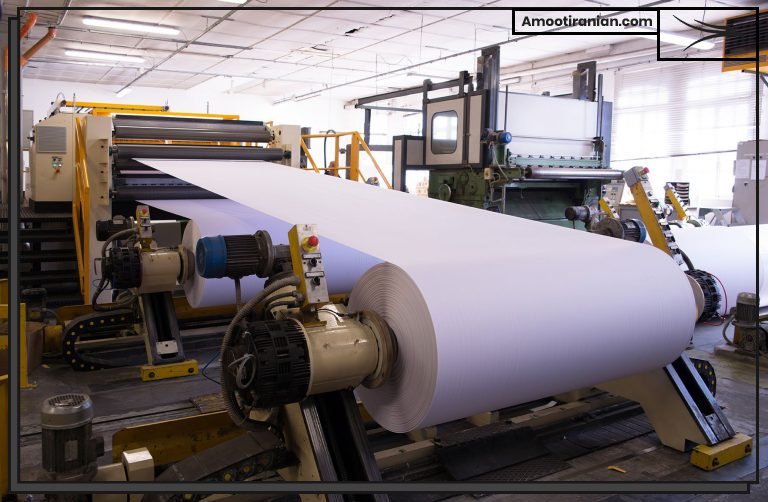
9_Paper production
Sulfur is used in various stages of paper production, from pulping to bleaching, to improve the quality and properties of paper products.
One of the main uses of sulfur in the paper industry is in the production of pulp, the raw material used to make paper.
.

.
Sulfur-based chemicals, such as sodium sulfite and sodium bisulfite, are commonly used in the pulping process to remove lignin from wood fibers and break down the cellulose into smaller fibers.
This process is known as the sulfite pulping process and is used to produce high-quality, lightweight paper products such as tissue paper, printing paper, and packaging paper.
10_Batteries
Sulfur is being investigated as a potential material for use in battery production, specifically in the development of high-energy-density lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries.
Li-S batteries have the potential to offer a higher energy density and lower cost compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries, making them an attractive option for use in electric vehicles and other energy storage applications.

In Li-S batteries, sulfur is used as the cathode material, which is the positive electrode that stores and releases electrons during charging and discharging.
During discharge, the lithium ions in the anode move towards the cathode and react with the sulfur to form lithium sulfide and release electrons. During charging, the process is reversed, and the lithium ions move back to the anode.
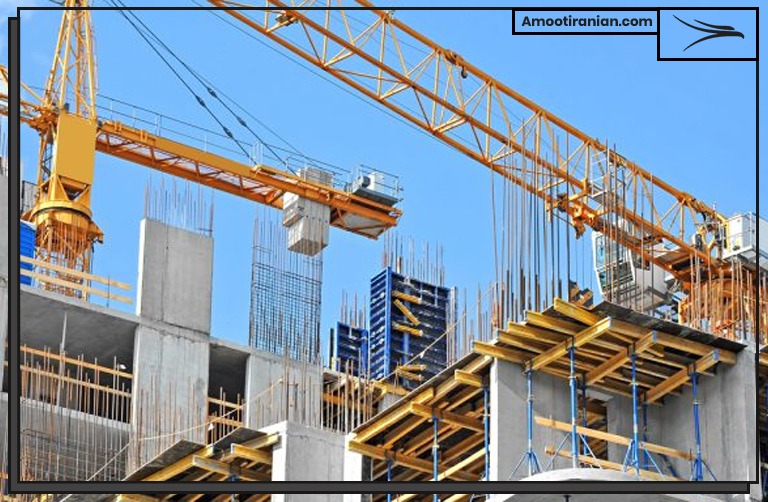
11_Construction industry
Sulfur is used in various ways in the construction industry, primarily in the production of construction materials such as concrete and asphalt.
One of the main uses of sulfur in the construction industry is as a component in the production of sulfur concrete, a high-strength, durable material that is resistant to chemical and thermal degradation. Sulfur concrete is made by mixing sulfur with aggregate materials such as sand and gravel, and it is used in a range of construction applications, including bridge decks, industrial flooring, and pipe supports.
Another use of sulfur in the construction industry is in the production of asphalt, a common material used for road construction and paving.
Sulfur is added to asphalt as a modifier, which helps to improve its properties, such as resistance to oxidation, cracking, and deformation under high temperatures.
Sulfur-modified asphalt is used in a range of construction applications, including road paving, roofing, and waterproofing.
Sulfur is also used in other construction materials, such as drywall joint compounds, adhesives, and sealants. In these applications, sulfur is used as a filler or as a component that imparts specific properties, such as improved adhesion, flexibility, or fire resistance.
12_Personal care products
Sulfur has been used for centuries as a treatment for various skin conditions, including acne, eczema, psoriasis, and seborrheic dermatitis.
Sulfur works by reducing inflammation, unclogging pores, and killing bacteria that contribute to acne and other skin conditions.
It also has keratolytic properties, which means that it can help to remove dead skin cells and promote the growth of healthy new skin cells.
.

.
Sulfur is typically used in skin care products as a topical treatment, either in the form of creams, lotions, or masks.
It is often combined with other ingredients, such as salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or retinoids, to enhance its efficacy and reduce potential side effects.
Sulfur-based skin care products are generally safe and well-tolerated, although some people may experience mild irritation or dryness.
Overall, sulfur is a popular and effective ingredient in skin care products for treating a range of skin conditions.
However, it is important to use sulfur-based products as directed and to consult with a dermatologist if you have any concerns or experience any adverse reactions.
13_Dyes
Overall, sulfur has a wide range of applications in different industries, making it an important element for the modern world.
Sulfur dyes are used in the textile industry to dye cotton, wool, and other fibers.
.

.
Sulfur Compounds
Sulfur is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is a non-metallic element that is essential for life and has a range of important industrial and commercial applications.
Sulfur compounds, which are compounds that contain sulfur, are particularly important due to their wide range of uses in various industries.
One of the most well-known sulfur compounds is hydrogen sulfide (H2S), which is a gas that has a characteristic odor of rotten eggs. Hydrogen sulfide is produced naturally by bacteria that break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, and it is also a byproduct of industrial processes such as oil and gas drilling, pulp and paper production, and wastewater treatment.
.
.
Despite its unpleasant odor, hydrogen sulfide has important industrial applications, such as in the production of sulfuric acid and as a reducing agent in metal refining.
Another important class of sulfur compounds is sulfides, which are compounds that contain the S2- ion. Sulfides are found in a range of minerals, including pyrite (FeS2), which is commonly known as fool’s gold, and galena (PbS), which is the primary ore of lead.
Sulfides also have important industrial applications, such as in the production of metal alloys and as a source of sulfur in the production of sulfuric acid.
Sulfur also forms a range of important organic compounds, such as thiol (R-SH) and sulfonic acid (R-SO3H).
Thiols, also known as mercaptans, are organic compounds that contain a sulfur atom and a hydrogen atom. They have a characteristic odor that is often described as being similar to that of garlic or onions.
Thiols have a range of industrial applications, such as in the production of pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and rubber products.
Sulfonic acids are organic compounds that contain a sulfur atom, a hydroxyl group (-OH), and an alkyl or aryl group.
They have a range of important industrial applications, such as in the production of detergents, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. Sulfonic acids are also used as catalysts in a range of chemical reactions.
Sulfur compounds also play an important role in biological systems. For example, cysteine and methionine are amino acids that contain sulfur and are essential components of proteins.
Sulfur compounds are also involved in the biosynthesis of a range of molecules, such as glutathione, which is an antioxidant that helps to protect cells from damage.
In conclusion, sulfur compounds are a diverse and important class of compounds that have a wide range of industrial, commercial, and biological applications. From hydrogen sulfide to organic thiols and sulfonic acids, sulfur compounds play an important role in a range of chemical reactions and processes.
With ongoing research and development, it is likely that sulfur compounds will continue to play an important role in a range of industries for years to come.
.
The Quality Iran & Turkmenistan Sulfur at Amoot Iranian
Amoot Iranian Trading Company is an old and experienced supplier and exporter of various types of sulfur including granular, powder, and lump to numerous countries across the globe.
Both the sulfur of Iran and Turkmenistan are available in Amoot Company and all transportation steps and custom clearance can be handled by Amoot team from the beginning to the end.
Amoot Iranian Trading Company takes pride in providing high-quality sulfur products to meet the diverse needs of its clients. The company has a strong supply chain network and works closely with reliable producers to ensure the quality and consistency of its sulfur products.

In addition to sulfur, Amoot Company also supplies other chemical products such as minerals, urea, cement, clinker, and gypsum powder. The company is committed to providing its customers with competitive prices and timely delivery.
Amoot Company has a team of experienced professionals who are knowledgeable about the global market and regulatory requirements. They are available to assist clients with all aspects of the ordering process, from product selection to custom clearance and transportation.
The company’s dedication to customer satisfaction has earned it a reputation as a trustworthy and reliable supplier. Amoot Iranian Trading Company is always looking for new opportunities to expand its market reach and establish long-term partnerships with its clients.
We are working and endeavoring to make the best opportunities for you!
If you like, we can send the sulfur price and details for you via email, WhatsApp, Telegram, WeChat, or any other messenger you like.
You can have online meeting with our experts and managers. Vising the sulfur stock in Bandar Abbas city of Iran is also possible at any time you wish.
