.

.
Signs of Sulfur Deficiency in Plants
.
| Signs of Sulfur Deficiency | . | Description |
|---|---|---|
Stunted Growth |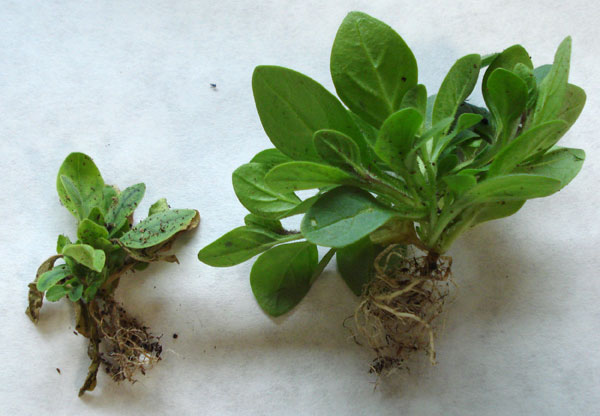  | Sulfur is required for the synthesis of amino acids and proteins, which are crucial for plant growth. . A deficiency of sulfur can lead to stunted growth of the plant. . |
Yellowing of Leaves | Sulfur is a key component of chlorophyll, which gives leaves their green color. . A lack of sulfur can cause yellowing of leaves, starting with the younger leaves. . | |
Delayed Maturity |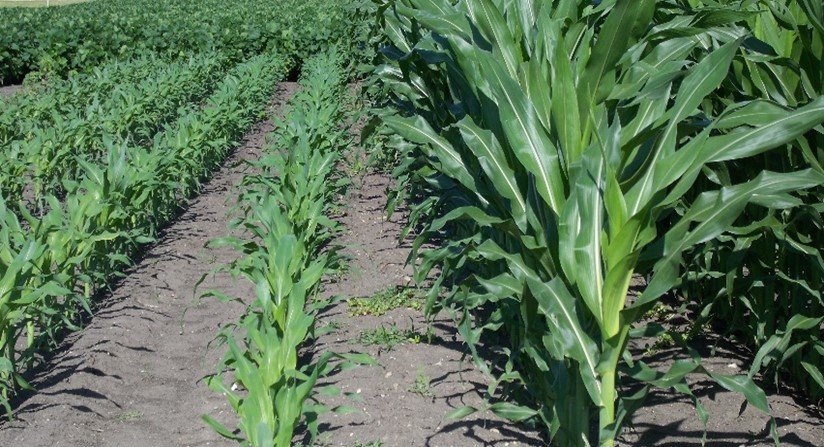  | Sulfur deficiency can delay the maturity of plants, leading to a longer time to harvest. . |
Reduced Crop Yield |  | Since sulfur is needed for many metabolic processes, a deficiency can cause reduced crop yield, as plants may not be able to produce as much fruit or grain. . |
Poor Quality of Produce |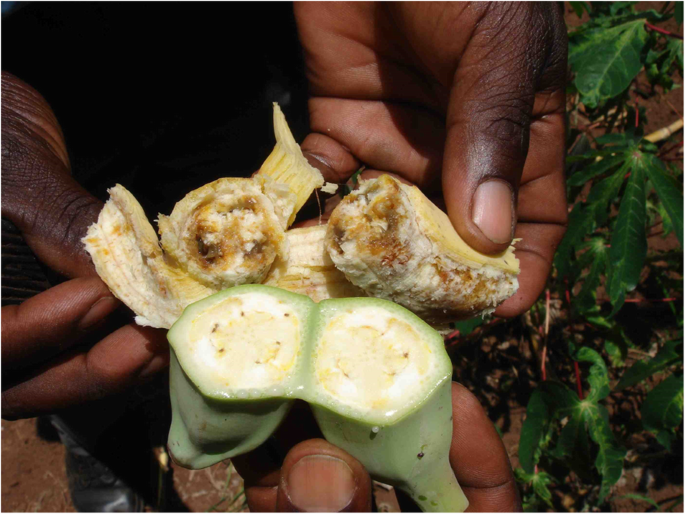  | Plants deficient in sulfur may produce produce that is smaller, misshapen, or discolored, as they may not have sufficient sulfur to synthesize the compounds needed for healthy growth. . |
Reduced root growth |  | Sulfur deficiency can also affect root growth, leading to smaller and shallower root systems. . This can limit the plant’s ability to take up water and nutrients from the soil. . |
Increased susceptibility to disease | Plants deficient in sulfur may be more susceptible to diseases and pests, as their weakened state can make them more vulnerable to attacks. . | |
Altered flavor and aroma |  | Sulfur is involved in the production of certain compounds that contribute to the flavor and aroma of fruits and vegetables. . A deficiency can lead to altered taste and smell of the produce. . |
.

.
.
How Do You Test for Sulfur Deficiency?
.
| Method | . | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Soil testing |  | Testing the sulfur content of the soil to determine if it’s low. . It may indicate the need for sulfur fertilizer or other soil amendments. . |
| Plant tissue analysis |  | Testing the sulfur content of plant tissue to determine if the plant is deficient in sulfur. A sample of the plant tissue is analyzed in a laboratory. . |
| Visual inspection | 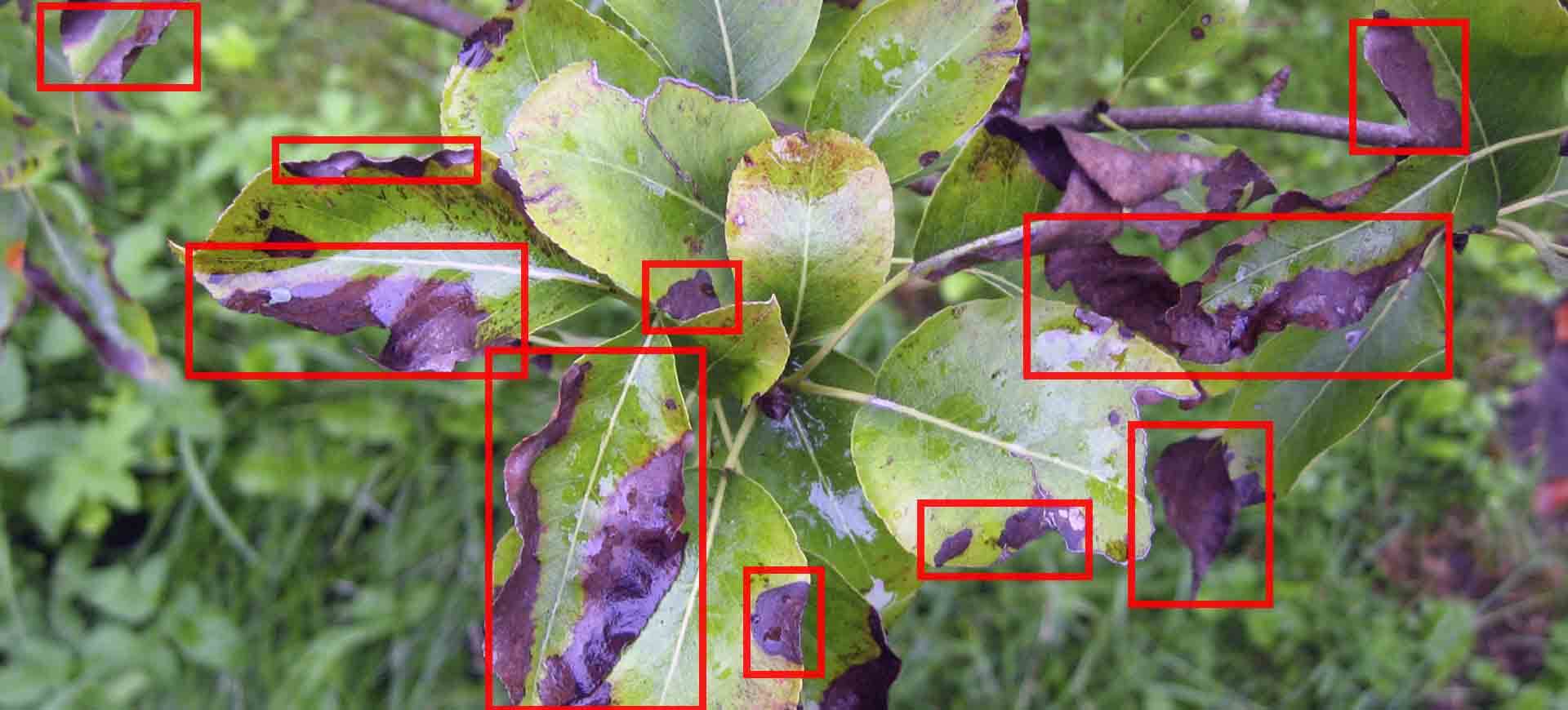 | Observing the plant for visual symptoms of sulfur deficiency, such as: 1. yellowing of leaves 2. stunted growth .. |
| Field experiments |  | Monitoring the growth and health of plants over time after adding sulfur fertilizer to plants that show symptoms of sulfur deficiency. . |
.

.
It’s important to note that sulfur deficiency can be difficult to diagnose, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other nutrient deficiencies or plant diseases.
Therefore, a combination of these methods is often used to confirm sulfur deficiency in plants.
.
What Causes Plants to Have Low Levels of Sulfur?
.
| Cause | Description |
| Low sulfur content in soil | If the soil lacks sulfur, the plants growing in that soil will also be deficient in sulfur. This can occur in soils that have low organic matter or that have been leached of sulfur through heavy rain or irrigation. |
| Soil pH | The availability of sulfur in the soil can be affected by soil pH. In acidic soils (pH below 6.0), sulfur is more available to plants, while in alkaline soils (pH above 7.0), sulfur may be less available. |
| Insufficient sulfur fertilization | If sulfur is not added to the soil in sufficient amounts through fertilization, the plants may not have enough sulfur to grow and function properly. |
| High nitrogen fertilization | High nitrogen fertilization can lead to an imbalance in the sulfur-to-nitrogen ratio in the plant, which can result in sulfur deficiency. This is because sulfur is needed for the synthesis of proteins, and a high nitrogen supply can increase the demand for sulfur. |
| Reduced sulfur dioxide emissions | Sulfur dioxide emissions from industrial sources can contribute to the atmospheric sulfur that can be deposited on the soil and taken up by plants. Reductions in these emissions can lead to lower sulfur deposition and availability to plants |
.

.
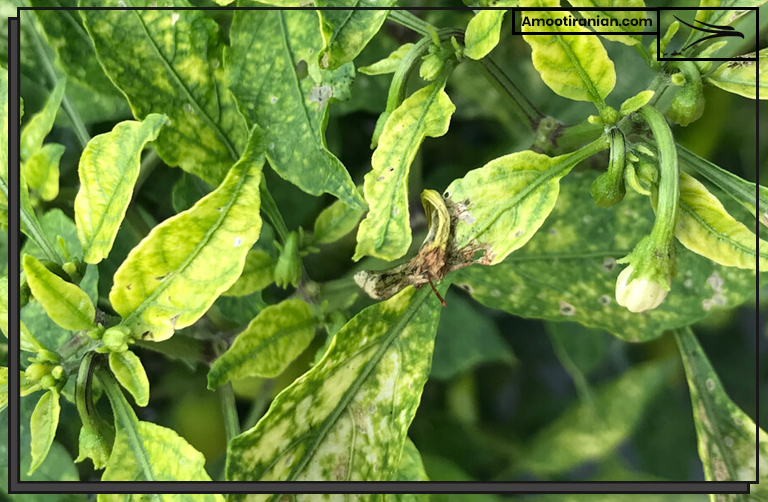
Where Does Deficiency of Sulphur First Appear?
The deficiency of sulfur in plants first appears in the newer growth, typically the younger leaves, because sulfur is a mobile nutrient in plants, which means that it can be moved from older tissues to support the growth of newer tissues.
.
As a result, sulfur deficiency symptoms tend to show up first in the young, actively growing parts of the plant, while older leaves may remain green and healthy-looking.
This can include yellowing of the leaves or stunted growth, depending on the severity of the deficiency.
.
Does Sulphur Deficiency Cause Chlorosis?
Yes, sulfur deficiency can cause chlorosis in plants.
.
Chlorosis is a condition where the leaves of a plant turn yellow due to a lack of chlorophyll, which is the pigment responsible for the green color of leaves.
.

.
Sulfur is essential for the formation of chlorophyll, and a deficiency in sulfur can lead to reduced chlorophyll synthesis, resulting in chlorosis.
The yellowing of the leaves is typically most noticeable in the newer growth, such as the young leaves and shoot tips, which have the highest demand for sulfur to support their growth.
.
How Do You Fix Sulfur Deficiency in Plants?
.
| Method | Description | |
| Applying sulfur fertilizer | Applying a sulfur-containing fertilizer can help to increase the availability of sulfur in the soil and improve plant growth. Sulfur can be applied in the form of elemental sulfur, sulfate-containing fertilizers, or organic matter such as compost or manure. . | |
| Adjusting soil pH |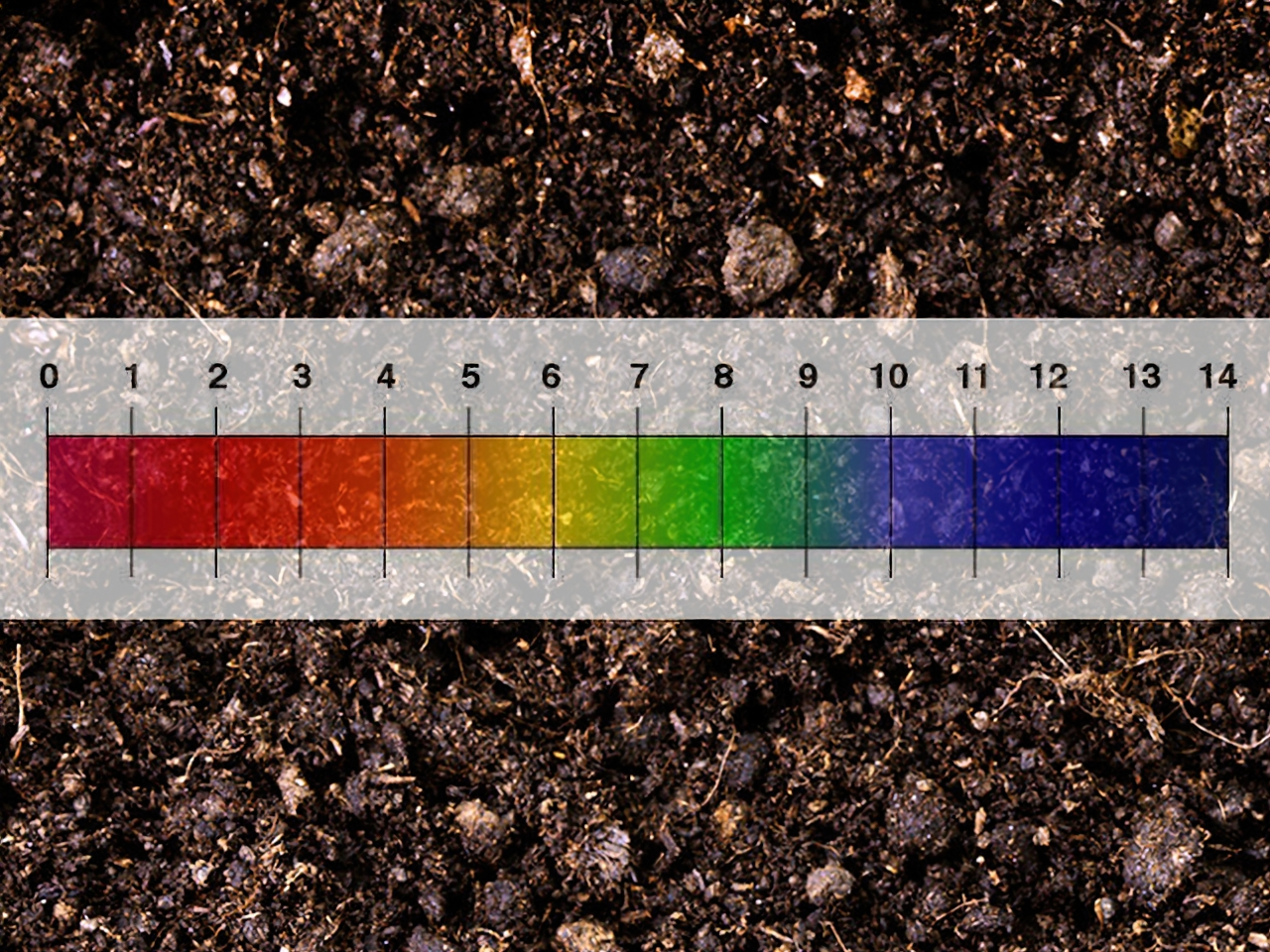  | Soil pH can affect the availability of sulfur in the soil. If the soil is too alkaline, it may be beneficial to lower the pH to a more acidic level to make sulfur more available to plants. This can be done by adding soil amendments such as sulfur or organic matter. . |
| Foliar spray |  | A foliar spray containing sulfur can provide a quick fix to plants showing symptoms of sulfur deficiency. The spray can be applied directly to the leaves of the plant, and the sulfur can be absorbed by the plant and used to support growth. . |
| Crop rotation |  | Planting crops that improve soil fertility, such as legumes, in a rotation with sulfur-demanding crops can help to maintain adequate sulfur levels in the soil. . |
| Soil amendment |  | Adding organic matter such as compost or manure can help to improve soil fertility and increase the availability of sulfur to plants over time. . |
.

.
It’s important to note that the method used to fix sulfur deficiency may depend on:
- the severity of the deficiency
- the soil conditions
- the specific needs of the plant species
.
It’s recommended to consult with a local extension service or a plant specialist for specific recommendations on how to address sulfur deficiency in your plants.
.
How Can You Tell the Difference in a Nitrogen or Sulfur Deficiency?
.
| Symptom | Nitrogen Deficiency | Sulfur Deficiency |
 |  | |
Leaf Color | Pale green or yellow | Yellow or pale green |
Location of Symptoms | Older leaves first, progressing to younger leaves | Newer leaves first, progressing to older leaves |
Leaf Size | Leaves are smaller than normal | Leaves may be smaller than normal, but not always |
Leaf Shape | Leaves may be thin and spindly | Leaves are typically normal in shape |
Stem Growth | Stems may be weak and spindly | Stems are typically normal |
Flowering and Fruiting | Reduced or delayed flowering and fruiting | Reduced or delayed flowering and fruiting |
Other Symptoms | Plants may appear stunted or have reduced growth | Plants may have a sulfur-like odor |
.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of nitrogen and sulfur deficiency can overlap, and other nutrient deficiencies or environmental factors can also cause similar symptoms.
Therefore, it’s recommended to perform a soil test and consult with a local extension service or a plant specialist to confirm the nutrient deficiency and determine the best course of action.
.

.
What Happens If Plants Get Too Much Sulfur?
.
While sulfur is essential for plant growth, too much sulfur can be harmful to plants. Excess sulfur can lead to a buildup of toxic compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide and sulfite, which can damage plant tissues and inhibit growth.
.
Symptoms of excess sulfur in plants may include:
- Dark green leaves
- Reduced growth
- Reduced fruit or flower production
- Stunted growth
- Browning or yellowing of leaves
- Burning or necrosis of leaf edges
.

.
“The Perils of Over-Fertilizing Plants and Trees“
.
If you suspect that your plants have been over-fertilized with sulfur or if you notice these symptoms, it’s important to stop adding sulfur fertilizer and irrigate the soil with clean water to flush out excess sulfur.
It’s also recommended to consult with a local extension service or a plant specialist for advice on how to address excess sulfur in your plants.
.
Which Plants Love Sulphur?
.
| Plant | Description | Sulfur Requirements | |
| Brassicas |  | Members of the cabbage family, including: 1. cabbage 2. broccoli 3. cauliflower | High |
| Alliums |  | Plants in the onion family, including: 1. garlic 2. onions 3. shallots | High |
| Legumes |  | Plants in the bean family, including: 1. peas 2. beans | Moderate |
| Corn |  | A cereal crop grown for its edible grains | Moderate |
| Sunflowers |  | A plant grown for its seeds or oil | Low to moderate |
| Grapes |  | A fruit-bearing vine used to make wine | Low |
.
It’s important to note that the sulfur requirements of plants can vary depending on:
- the specific cultivar
- soil conditions
- other environmental factors
.
Is Sulfur Acidic or Alkaline?
Sulfur itself is a non-metal element and is neither acidic nor alkaline. However, when sulfur combines with other elements to form compounds, the resulting compound can be either acidic or alkaline.
.
.
For example, sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is a highly acidic compound that is commonly used in fertilizers and industrial applications.
On the other hand, calcium sulfate (CaSO4), also known as gypsum, is a neutral to slightly alkaline compound that is often used to improve soil quality and water retention in gardening and agriculture.
.
In general, the pH of a sulfur-containing compound will depend on the other elements and molecules it is combined with.
.
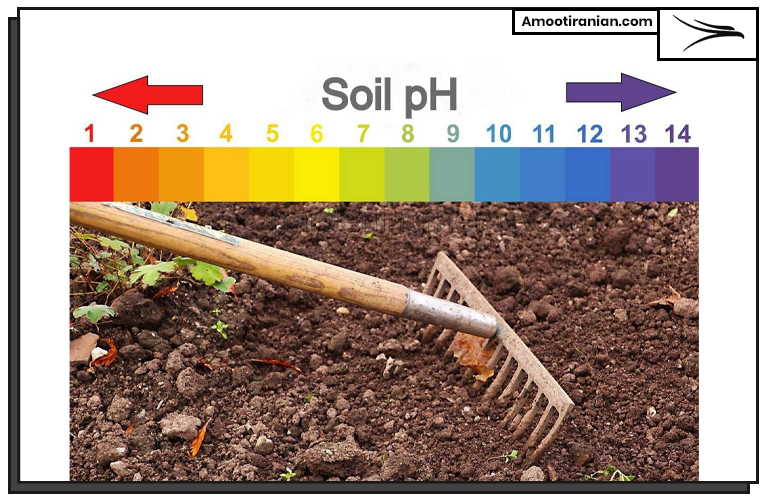
.
Does Sulfur Fertilizer Lower pH?
Yes, some sulfur-containing fertilizers can lower the pH of the soil over time. This is because sulfur reacts with water to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This is a strong acid that can decrease the pH of the soil.
.
.
When sulfur-containing fertilizers, such as ammonium sulfate or elemental sulfur, are applied to the soil, the sulfur in these fertilizers reacts with soil moisture to form sulfuric acid.
This acid can react with and release minerals, such as aluminum and manganese, from the soil particles.
This can further lower the soil pH.
.
However, the extent of pH reduction will depend on several factors, including:
- the amount and type of sulfur-containing fertilizer used
- soil type and properties
- environmental conditions
.
It’s important to regularly monitor the soil pH when applying sulfur-containing fertilizers and adjust the fertilizer application rates accordingly to maintain optimal pH levels for plant growth.
.
You can check the optimal ph level for plants HERE.
.

.
