.

.
How Many Types of Fertilizers Are There?
There are three primary types of fertilizers, based on their nutrient composition:
1. Nitrogenous fertilizers: These fertilizers contain nitrogen as their primary nutrient. Examples include ammonium nitrate, urea, ammonium sulfate, and calcium cyanamide. 2. Phosphatic fertilizers: These fertilizers contain phosphorus as their primary nutrient. Examples include superphosphate, triple superphosphate, and diammonium phosphate. 3. Potassic fertilizers: These fertilizers contain potassium as their primary nutrient. Examples include potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, and potassium nitrate.
.
In addition to these primary types, there are also fertilizers that contain a combination of these nutrients, as well as secondary nutrients like:
- calcium
- magnesium
- sulfur
These are called NPK fertilizers, as they contain a combination of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
.
What Is Potassium Fertilizer?
Potassium fertilizer is a type of fertilizer that contains potassium as its primary nutrient.
.

.
As mentioned before, potassium is one of the three primary macronutrients that plants need to grow, along with nitrogen and phosphorus.
Potassium plays a key role in many plant processes, including photosynthesis, water uptake and transportation, and stress tolerance.
.

.
Potassium fertilizer can come in many forms, including:
- Potassium chloride
- Potassium sulfate
- Potassium nitrate
.
It is commonly used in agriculture to improve crop yields and overall plant health.
Potassium fertilizer can be applied directly to the soil or through foliar spraying, depending on the specific crop and its nutrient needs.
.
What Is the Example of Potassic Fertilizer?
.

.
1. Examples of Potassic Fertilizers
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
- Potassium sulfate (K2SO4)
- Potassium nitrate (KNO3)
- Potassium magnesium sulfate (K2SO4.2MgSO4)
These fertilizers contain significant amounts of potassium, which is an essential nutrient for plant growth and development.
.
2. What Is the Most Commonly Used Potassic Fertilizer?
Potassium chloride is the most commonly used potassic fertilizer, but the choice of fertilizer will depend on the specific crop and soil conditions.
.
3. Which of Potassic Fertilizers Has the Most Amount of Potassium?
Potassium chloride (KCl) typically has the highest amount of potassium among the commonly used potassic fertilizers.
.
It typically contains around 60% to 62% potassium, depending on the grade and source.
Potassium sulfate (K2SO4) usually contains around 50% potassium, potassium nitrate (KNO3) contains around 44% potassium, and potassium magnesium sulfate (K2SO4.2MgSO4) contains around 22% potassium.
However, the choice of fertilizer will depend on various factors, including the specific crop requirements and soil conditions, and it’s important to follow recommended application rates to avoid over-application and potential negative impacts on the environment.
.
Potassium Fertilizer Benefits
.

.
1. Is potassium good or bad for plants?
The Benefits of Potassic Fertilizers
| Benefits of Potassic Fertilizers | Explanation |
| Promotes root growth | Potassium helps regulate water movement within plant tissues. It can lead to stronger and healthier root systems. |
| Improves stress tolerance | Potassium can help plants withstand: 1. drought 2. extreme temperatures 3. other environmental stressors |
| Enhances fruit quality | Potassium can improve the color, size, and flavor of fruits and vegetables. |
| Increases disease resistance | Potassium can help plants resist certain diseases and pests by strengthening cell walls and improving overall plant health. |
| Improves yield | Adequate potassium levels can increase crop yields by improving plant growth and development. |
| Helps with nutrient uptake | Potassium can improve the uptake and utilization of other essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus. |
.

.
It’s important to note that the benefits of potassic fertilizers may vary depending on the specific crop, soil conditions, and application rates.
It’s recommended to consult with a local agronomist or agricultural extension service to determine the appropriate fertilizer type and application rate for a specific crop and field.
.
2. What Plants Benefit from Potassium Fertilizer?
Many different types of plants benefit from potassium fertilizer, including:
- Fruits and vegetables – Potassium can improve the size, color, and flavor of fruits and vegetables, as well as help them resist disease and pests. Examples of potassium-loving fruits and vegetables include tomatoes, potatoes, peppers, citrus fruits, berries, and melons.
- Grains and cereals – Potassium is important for grain and cereal crops, as it can improve stalk strength and help the plant withstand wind and rain. Examples of potassium-loving grains and cereals include corn, wheat, rice, and barley.
- Ornamental plants – Potassium can improve the overall health and appearance of ornamental plants, as well as help them resist disease and pests. Examples of potassium-loving ornamental plants include roses, chrysanthemums, and geraniums.
- Turfgrass – Potassium is important for maintaining healthy turfgrass, as it can improve drought tolerance, disease resistance, and overall vigor.
.
It’s important to note that different crops may have varying requirements for potassium.
It’s essential to follow recommended application rates to avoid over-application, which can cause negative impacts on the environment.
.
What Are the Effects of Too Much Potassium In Plants?
While potassium is an essential nutrient for plant growth and development, too much of it can have negative effects on plants.
.

.
The effects of excessive potassium can vary depending on the plant species, soil type, and other environmental factors, but some common effects include:
- Reduced uptake of other essential nutrients: High levels of potassium can interfere with the uptake of other essential nutrients, such as magnesium, calcium, and nitrogen. This can lead to nutrient imbalances and deficiencies, even if these nutrients are present in the soil.
- Reduced water uptake: High levels of potassium can affect the plant’s ability to take up water, leading to water stress and reduced growth.
- Reduced root growth: Excessive potassium can lead to reduced root growth, which can limit the plant’s ability to take up nutrients and water from the soil.
- Reduced photosynthesis: High levels of potassium can affect the plant’s ability to carry out photosynthesis, which can lead to reduced growth and yield.
- Increased susceptibility to disease: Excessive potassium can make plants more susceptible to certain diseases, such as root rot and leaf spot.
.
It’s important to note that the effects of excessive potassium can be similar to those of other nutrient imbalances or toxicities, and proper soil testing and nutrient management are essential to prevent these issues.
.
How Is Potassium Fertilizer Used?
.

.
1. How Do You Add Potassium To Soil?
Potassium fertilizer can be applied in various ways, depending on the specific crop and its nutrient requirements. Here are some common methods of using potassium fertilizer:
- Soil application: Potassium fertilizer can be applied to the soil before planting or during the growing season to provide the necessary nutrients to the plants. The fertilizer can be broadcast across the soil surface, applied in bands or rows, or incorporated into the soil through tillage.
- Foliar application: In some cases, potassium fertilizer can be applied directly to the leaves of the plant. This is done by spraying a diluted solution of the fertilizer onto the foliage. Foliar application can be particularly useful in situations where the soil is deficient in potassium or the plant is under stress.
- Fertigation: It is the process of applying fertilizer through an irrigation system. In this method, a soluble form of potassium fertilizer is injected into the irrigation water and distributed evenly across the field.
- Side-dressing: Side-dressing involves applying potassium fertilizer in a band beside the plant rows during the growing season. This helps to ensure that the fertilizer is placed close to the root zone of the plants, where it can be most readily absorbed.
.

.
Overall, the specific method of using potassium fertilizer will depend on a variety of factors, including:
- The crop type
- Soil conditions
- The stage of growth
.
It’s important to follow recommended application rates and timing to avoid over-application and potential negative impacts on the environment.
.
2. What Is The Fastest Way To Add Potassium To Soil?
There are several ways to add potassium to soil quickly, including:
- Potassium fertilizer: The most direct and effective way to add potassium to soil is by using a potassium fertilizer. These fertilizers are available in various forms, including potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, and potassium nitrate. They can be applied to the soil directly or mixed with water and sprayed onto the plant foliage.
- Organic matter: Organic matter such as compost, manure, or wood ash can also be used to add potassium to soil. These materials release potassium slowly over time as they break down, but they can help improve soil structure and fertility as well.
- Greensand: Greensand is a natural mineral that is high in potassium and other micronutrients. It can be added to soil as a slow-release fertilizer or mixed with water and sprayed onto plant foliage.
- Potassium-rich plants: Certain plants are naturally high in potassium, such as comfrey and seaweed. These plants can be grown and then chopped up and added to soil as a natural potassium fertilizer.
.
It’s important to note that adding too much potassium to soil can be harmful to plants, so it’s important to follow recommended application rates and conduct soil testing to ensure that nutrient levels are balanced.
.
3. When Should I Fertilize with Potassium?
The timing of potassium fertilizer application depends on several factors, such as:
- The type of crop
- Soil type
- Climate
Generally, it’s good to apply potassium fertilizer before or during planting, as this can help ensure that the nutrient is available to the plant throughout the growing season.
.
For annual crops, such as vegetables and grains, it’s often best to apply potassium fertilizer as a pre-plant or starter fertilizer, or split it into multiple applications throughout the growing season.
.
For perennial crops, such as fruit trees and vines, it’s common to apply potassium fertilizer in the fall after harvest or in the early spring before bud break.
.
In addition to timing, it’s important to consider the application method and rate, as well as the form of potassium fertilizer being used. It’s recommended to follow soil test recommendations and fertilization guidelines specific to the crop and region to ensure effective and efficient use of potassium fertilizer.
.
What Is The Largest Source Of Potassium In Soils?
The largest source of potassium in soils is the naturally occurring mineral called feldspar.
.
Feldspar is a common mineral in many types of rocks and soils, and it contains significant amounts of potassium.
Over time, feldspar breaks down into smaller particles through weathering and releases potassium into the soil.
Other sources of potassium in soils include minerals such as mica and clay, as well as organic matter such as compost and decaying plant material.
However, the amount of potassium available in soil can vary depending on factors such as soil pH, texture, and fertility, and it is important to manage soil fertility to ensure that potassium levels are adequate for plant growth.
.
Does Potassium Increase Soil Ph?
Potassium does not directly increase soil pH. In fact, in some cases, potassium can help to lower soil pH.
.
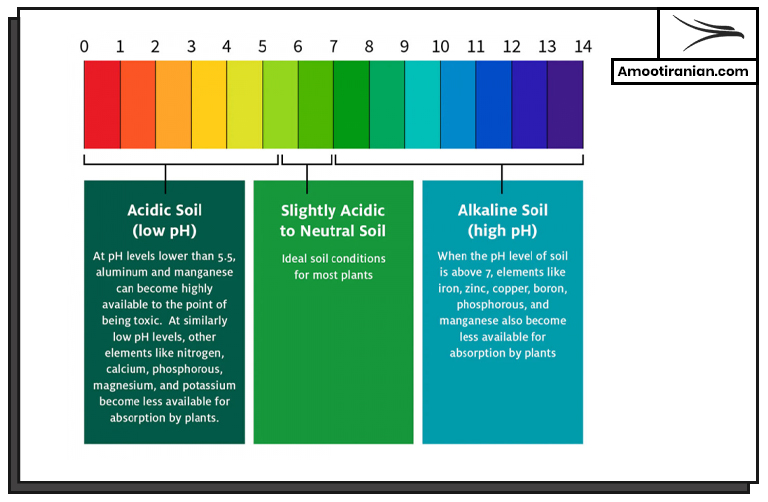
.
However, the use of certain potassium fertilizers, such as potassium carbonate, can indirectly raise soil pH because they release hydroxyl ions when they dissolve in soil water. These hydroxyl ions can react with hydrogen ions in the soil, which raises the soil pH.
.
Is potassium acidic or alkaline?
Potassium itself is not acidic or alkaline as it is a chemical element with a neutral pH.
.

.
It is important to note that the effect of potassium on soil pH will depend on several factors, including the type and form of potassium fertilizer used, the amount of fertilizer applied, and the soil type and composition.
Additionally, other factors such as the presence of other minerals or fertilizers in the soil can also influence soil pH.
