.

.
What are nutrient deficiencies?
Nutrient deficiencies are conditions where plants are not getting enough of one or more essential nutrients needed for healthy growth and development.
.
Essential nutrients include macronutrients like:
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese
.
When a plant experiences a nutrient deficiency, it can have a range of negative effects on its growth and health, such as stunted growth, yellowing or discolored leaves, reduced yields, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases. These signs are explained in next parts completely.
.
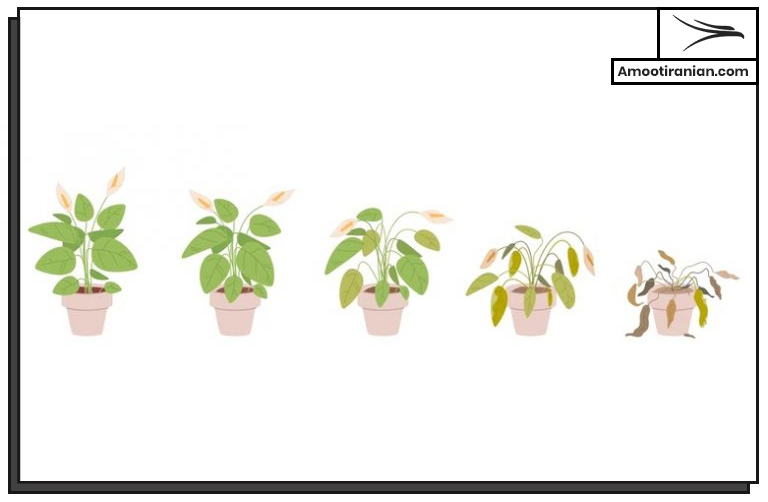
.
Nutrient deficiencies can occur for a variety of reasons, such as:
- Poor soil quality
- Improper fertilization
- Excessive water
- Drought conditions
- PH imbalances
.
It’s important to identify and address nutrient deficiencies in plants to ensure optimal growth and yield.
This may involve testing the soil and/or plant tissue to determine which nutrients are deficient and providing the plant with the necessary nutrients through fertilization or other means.
.
What Are The 3 Most Common Nutrient Deficiencies In Plants?
The three most common nutrient deficiencies in plants are:
1. Nitrogen deficiency
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth and development. A lack of nitrogen can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced yields.
2. Phosphorus deficiency
Phosphorus is important for root development and overall plant growth. A lack of phosphorus can lead to stunted growth, weak stems, and dark green or purple leaves.
3. Potassium deficiency
Potassium is essential for plant growth and development, as well as for regulating water balance in cells. A lack of potassium can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced resistance to stress and disease.
.
It’s important to note that the specific nutrient deficiencies that occur in plants can vary depending on the type of plant, soil type, and growing conditions.
Regular soil testing and plant monitoring can help identify any nutrient deficiencies and address them before they become a major problem.
.
How Do You Know If A Plant Is Nutrient Deficient?
.
| Symptoms | Image | Nutrient Deficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Yellowing or browning of leaves |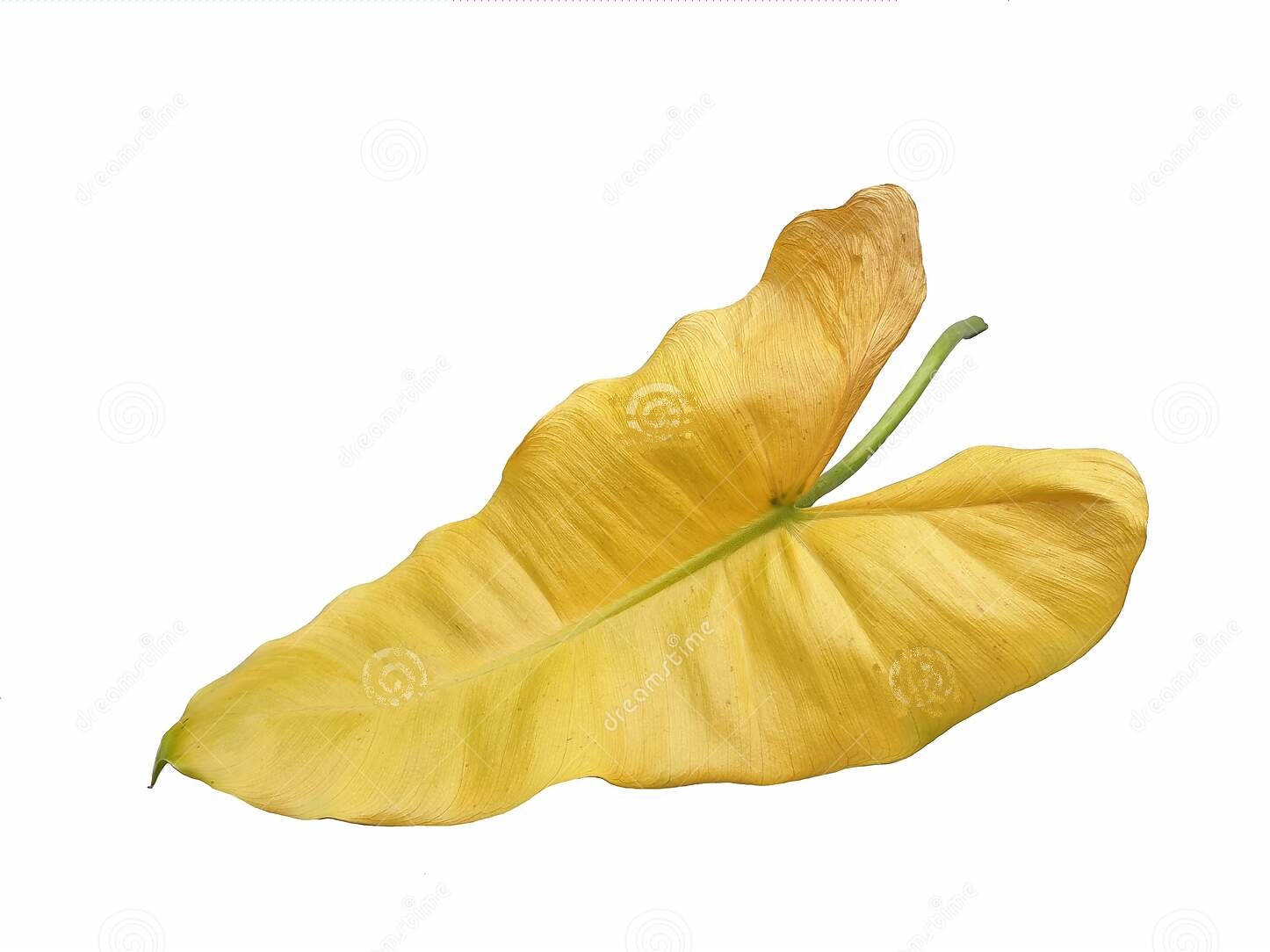  | Nitrogen, potassium, magnesium |
| Stunted growth |  | Nitrogen, phosphorus, magnesium |
| Weak stems |  | Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium |
| Poor fruit or flower development |  | Nitrogen, phosphorus |
| Leaf drop |  | Nitrogen, potassium |
| Discoloration |  | Iron (yellowing between veins), manganese (yellowing and browning of leaves) |
| Dark green leaves with purple tint |  | Phosphorus |
| Yellowing and curling of leaf edges |  | Potassium |
| Brown leaf edges |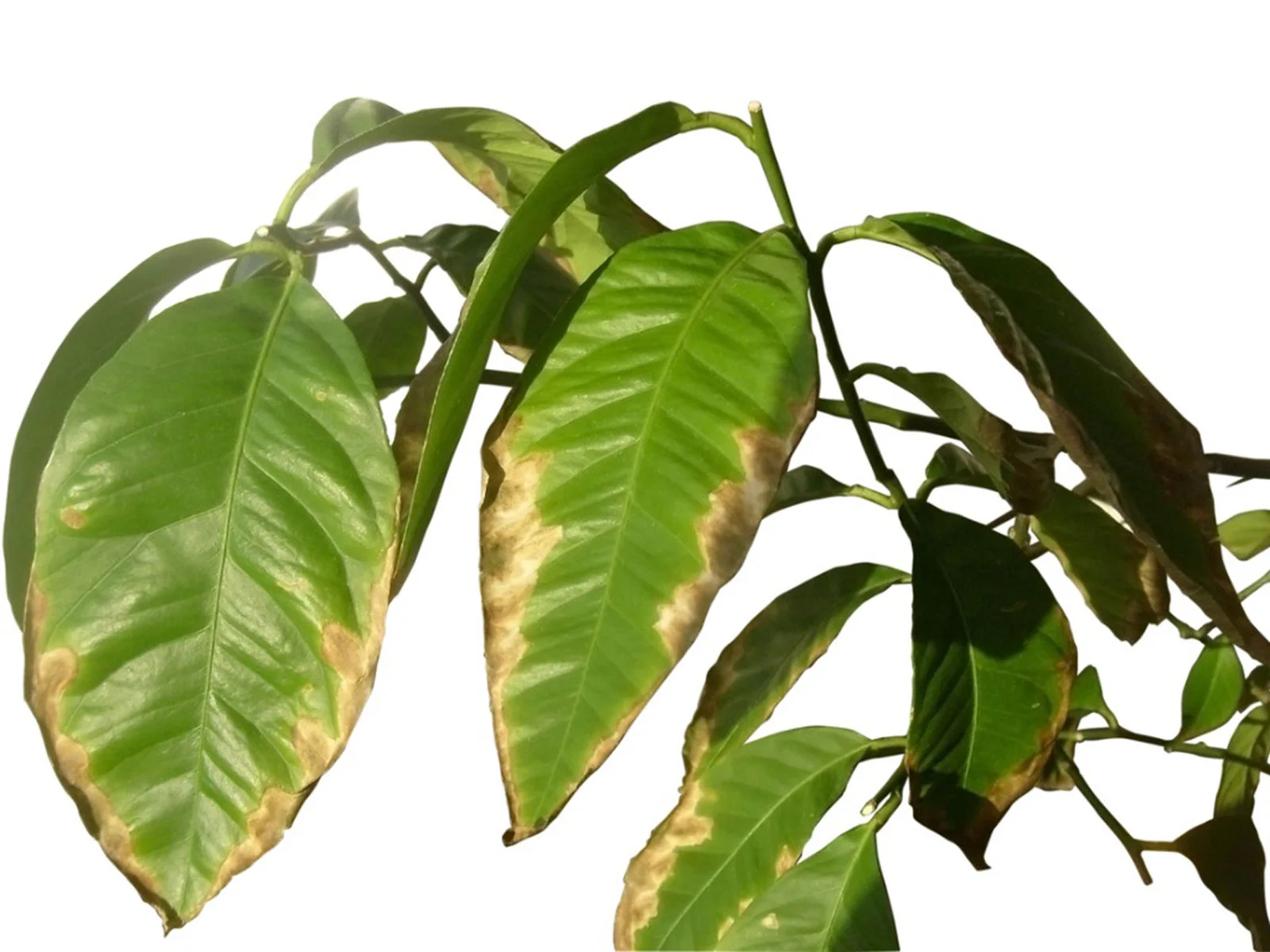  | Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, |
| Stunted growth, distorted or necrotic leaves |  | Calcium |
| Blossom end rot in fruit |  | Calcium |
| Yellowing between leaf veins (starting at the bottom of the plant) |  | M |
| Holes in leaves |  | Nitrogen |
| Leaves look burnt |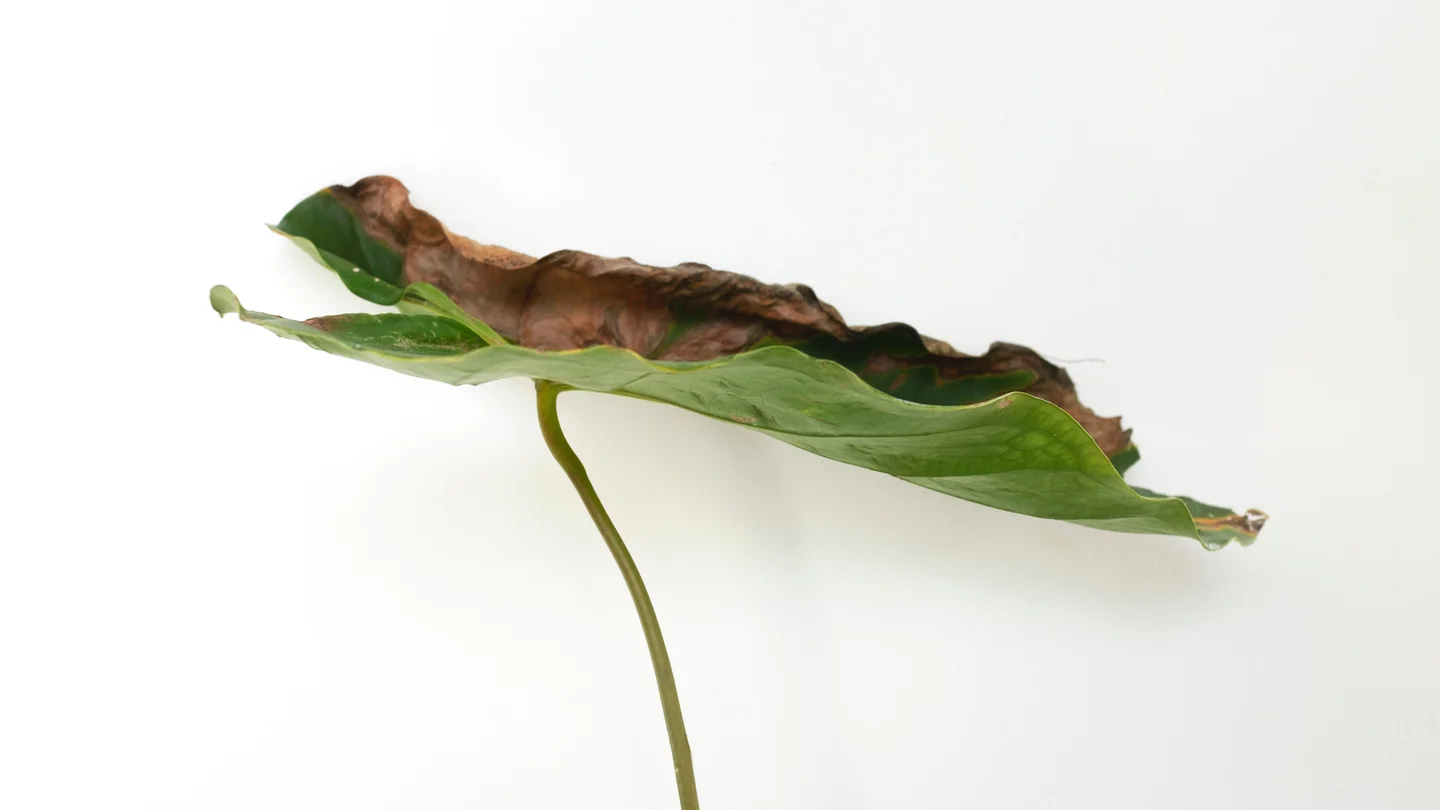  | Potassium or magnesium |
| Yellow or brown spots on leaves |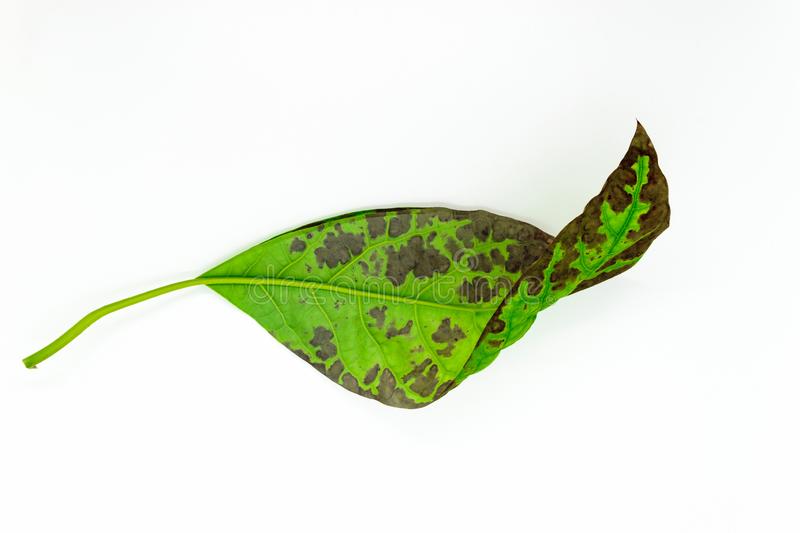  | Iron or magnesium |
.

.
What Are Solutions For Nutrient Deficiency In Plants?
.
There are several solutions for addressing nutrient deficiencies in plants, depending on the specific nutrient and the severity of the deficiency.
Here are some options:
1. Soil testing
Testing the soil can help identify which nutrients are deficient and guide the appropriate treatment.
.
2. Fertilization
Adding a balanced fertilizer containing the necessary nutrients can help address nutrient deficiencies. Fertilizers can be applied directly to the soil or sprayed onto the foliage.
.
3. Foliar feeding
This involves spraying a nutrient solution directly onto the leaves of the plant to provide a quick boost of nutrients.
.
4. Organic amendments
Organic materials such as compost, manure, and bone meal can be added to the soil to provide a slow-release source of nutrients.
.
5. Adjusting pH
Sometimes a nutrient deficiency can be caused by an imbalanced soil pH. Adjusting the pH to the appropriate level can help improve nutrient uptake.
.
6. Crop rotation
Planting different crops in a rotation can help replenish nutrients in the soil and prevent nutrient depletion.
