.
Urea is commonly used as a raw material in the production of urea-formaldehyde resin.
.

.
Which Resin Is Prepared from Urea and Formaldehyde?
Urea-formaldehyde (UF) resin is prepared from the reaction between urea and formaldehyde. It is a widely used thermosetting resin in industries such as woodworking, construction, and textiles, among others.
UF resin is often used as an adhesive or binder due to its strong bonding properties, water resistance, and low cost.
.
It is commonly used in the production of wood-based composite materials such as:
- particleboard
- medium-density fiberboard (MDF)
- plywood
.
UF resin is also used in the textile industry as a wrinkle-resistant finishing agent for cotton and other natural fibers. It can also be used in the production of paper, where it is added to the pulp to increase its strength and durability.
However, UF resin has some drawbacks. It emits formaldehyde gas during its curing process, which can be harmful to human health if not properly controlled.
Therefore, manufacturers of UF resin products must comply with strict regulations regarding formaldehyde emissions.
.

.
How Is Urea-Formaldehyde Resin Made?
There is a simplified table outlining the general process for making urea-formaldehyde resin:
| Step | Description |
| 1 | Urea is produced by reacting carbon dioxide and ammonia at a temperature between 135-200°C and a pressure of 70-230 atmospheres. |
| 2 | Formaldehyde is produced through the oxidation of methanol, which is produced by reacting carbon dioxide with hydrogen or extracted from petroleum. |
| 3 | The urea and formaldehyde are mixed in the presence of a catalyst, typically an acidic or basic catalyst. |
| 4 | The mixture is heated to a temperature between 70-100°C to initiate the reaction. |
| 5 | The resin is then cooled and stabilized to prevent further reaction. |
| 6 | The resin may be modified with other additives or modifiers, depending on the intended application. |
| 7 | The final product is packaged and shipped to customers for use in various industries. |
.
It is worth noting that the actual production process for urea-formaldehyde resin may vary depending on the specific manufacturer and the intended use of the resin.
.
What Is the Ratio of Urea and Formaldehyde to Produce Useful Resins?
The ratio of urea to formaldehyde in the production of urea-formaldehyde resin typically ranges from 1:2 to 1:2.2, with a slight excess of formaldehyde to ensure complete reaction.
This ratio allows for efficient methylolation of the urea at temperatures between 90-95°C, with the mixture being maintained under reflux.
The reaction generates heat and an exothermic reaction takes place, and the formation of the resin is completed after the exothermic reaction has subsided.
.

.
What Is the Use of Urea-Formaldehyde Resin?
.
Some common uses of urea-formaldehyde resin
Industry/Application | Use of Urea-Formaldehyde Resin |
| Wood-based composite materials | Adhesive/binder in the production of particleboard, medium-density fiberboard (MDF), and plywood |
| Textiles | Finishing agent to make fabrics wrinkle-resistant |
| Paper products | Added to pulp to increase strength and durability |
| Insulation | Binder in the production of thermal insulation materials |
| Electrical appliances | Used as a molding compound for switches, plugs, and other components |
| Automotive industry | Used in the production of automotive interior parts such as dashboards and door panels |
| Construction | Used in the production of various construction materials such as roofing tiles, wall panels, and flooring |
| Adhesives and sealants | Used as an adhesive in various applications such as woodworking and construction, as well as in the production of sealants and coatings |
| Agriculture | Used in the production of fertilizers to slow-release nitrogen |
| Personal care products | Used in the production of some cosmetics and personal care products such as nail polish and hair styling products |
.
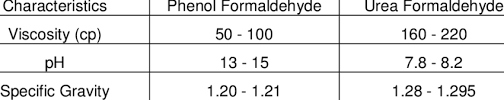
Which Is Better Urea-formaldehyde or Phenol Formaldehyde?
.
.
In general, phenol formaldehyde resins have better mechanical properties and water resistance compared to urea formaldehyde resins. Therefore, in most cases, phenol formaldehyde is considered to be a better option for producing particleboards and other composite wood products.
Phenol formaldehyde resins have a higher curing temperature, which leads to the formation of a more cross-linked and rigid polymer network. This results in better dimensional stability, higher strength, and improved resistance to moisture and heat.
On the other hand, urea formaldehyde resins have a lower curing temperature and a lower cost, making them more commonly used in the production of particleboards.
However, they have lower mechanical properties and are less resistant to moisture and heat compared to phenol formaldehyde.
.
Therefore, the choice of resin depends on the specific requirements of the application and the desired properties of the final product.
.
What Are the Disadvantages of Urea-formaldehyde Resin?
| Disadvantages of Urea-Formaldehyde Resin |
Lower HDT (Heat Deflection Temperature) – Urea-formaldehyde resin has a lower HDT than other resins, meaning that it deforms more easily when exposed to high temperatures. |
Lower Tensile Strength – Urea-formaldehyde resin has lower tensile strength compared to other resins, which makes it less suitable for applications that require high strength. |
Lower Flexural Modulus – Urea-formaldehyde resin has lower flexural modulus, which means it is more flexible and less stiff than other resins. |
Higher Water Absorption – Urea-formaldehyde resin has a higher water absorption rate, which can lead to dimensional changes, warping, and degradation of the product. |
Higher Mold Shrinkage – Urea-formaldehyde resin has a higher mold shrinkage rate, which can cause the product to shrink and deform during the curing process. |
Lower Surface Hardness – Urea-formaldehyde resin has lower surface hardness, which makes it more susceptible to scratches and wear. |
Lower Elongation at Break – Urea-formaldehyde resin has a lower elongation at break, which means it is less flexible and more likely to crack or break under stress. |
Lower Volume Resistance – Urea-formaldehyde resin has lower volume resistance, which can make it less suitable for use in electrical and electronic applications. |
