.
How to find out high purity sulfur?
How do you test the purity of sulfur?
How do you analyze Sulphur?
All methods available for sulfur purity analysis are explained in this page from the beginning to the end.
.

.
What Is Sulfur Purity Analysis?
Experts find out the granular sulfur purity analysis in the laboratory using a variety of analytical methods.
Here are some common techniques used to determine the purity of granular sulfur:
- Melting Point Analysis
- Elemental Analysis
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
- Titration
- Spectroscopy
.
Melting Point Analysis
The melting point of pure sulfur is around 119°C. Experts can measure the melting point of the granular sulfur and compare it to the known melting point of pure sulfur to determine the purity of the sample.
.

.
The procedure is as follow:
.
1_Placement: A small amount of granular sulfur is placed in a capillary tube.
.
2_Insertion: The capillary tube is inserted into a melting point apparatus.
.
3_Heating: The apparatus heats the sample at a controlled rate until the sulfur melts, and the temperature is recorded as the melting point.
.
4_Comparison: If the melting point of the sample is close to the known melting point of pure sulfur (119°C), it suggests that the sample is of high purity.
.
5_Impurities: If the melting point is lower than expected, it could indicate the presence of impurities in the sample.
.
6_Confirmation: The melting point can be affected by the particle size, shape, and packing of the sulfur crystals, so other analytical methods may be necessary to confirm purity.
.
Elemental Analysis
Elemental analysis can be performed by techniques such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) or inductively coupled plasma (ICP) spectroscopy. These techniques can provide quantitative measurements of the elemental composition of the sulfur sample, allowing experts to determine if there are any impurities present.
.
Here are the steps involved in elemental analysis of granular sulfur using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) or inductively coupled plasma (ICP) spectroscopy:
.
1_Sample Preparation: A small amount of the granular sulfur sample is taken and prepared for analysis. The sample is typically ground to a fine powder to ensure even distribution of the sulfur throughout the sample.
.
2_Instrument Calibration: The XRF or ICP instrument is calibrated using known standards to establish a baseline for the elements of interest.
.
3_Analysis: The prepared sulfur sample is analyzed using the XRF or ICP instrument. XRF detects the fluorescent X-rays emitted by the sample when it is exposed to high-energy X-rays, while ICP uses plasma to atomize the sample and produce ions, which are then detected by a mass spectrometer.
.
4_Quantification: The data obtained from XRF or ICP is processed using software that compares the measured intensities of the sample to the known standards. The concentration of each element in the sample can then be calculated.
.
5_Identification of Impurities: By comparing the elemental composition of the sample to the expected composition of pure sulfur, experts can identify the presence of any impurities in the sample.
.
Overall, elemental analysis can provide valuable information on the composition of granular sulfur, helping experts to determine its purity.
.
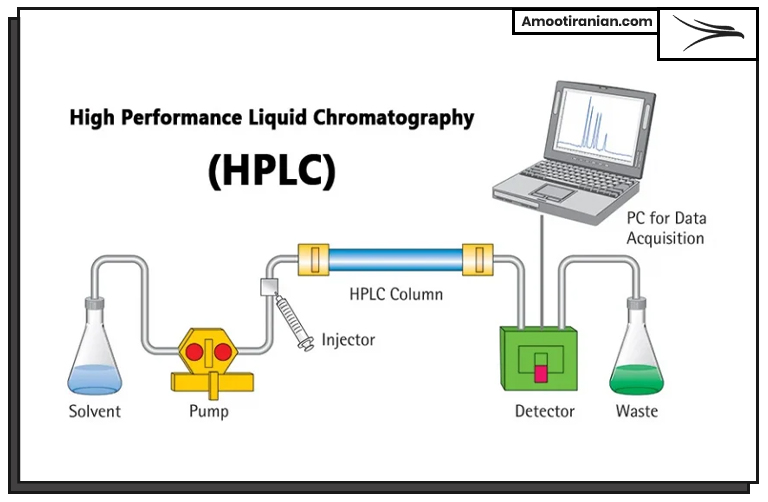
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
HPLC is a technique used to separate, identify, and quantify components in a mixture. By analyzing the components present in the sulfur sample, experts can determine the purity of the sample.
.
.
Here are the steps involved in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) for the analysis of granular sulfur:
.
1_Sample Preparation: A small amount of the granular sulfur sample is taken and prepared for analysis. The sample is typically dissolved in a solvent to form a solution.
.
2_Column Preparation: A chromatography column is selected based on the properties of the sample, such as its polarity and size. The column is then packed with a stationary phase material that interacts with the sample components.
.
3_Injection: The sample solution is injected into the column using a syringe or an automatic injector.
.
4_Separation: The sample components are separated as they move through the column due to their interactions with the stationary phase material. The components that interact more strongly with the stationary phase material take longer to pass through the column, resulting in separation.
.
5_Detection: The separated components are detected as they elute from the column using a detector, such as a UV-Vis spectrophotometer or a mass spectrometer. The detector generates a signal that is proportional to the amount of each component in the sample.
.
6_Quantification: The data obtained from the detector is processed using software that compares the measured signal to known standards. The concentration of each component in the sample can then be calculated.
.
7_Identification of Impurities: By comparing the components present in the sample to the expected components of pure sulfur, experts can identify the presence of any impurities in the sample.
.
Overall, HPLC can provide valuable information on the composition of granular sulfur, helping experts to determine its purity.
.
Titration
Titration is a technique used to determine the concentration of a substance in a solution by reacting it with a standard solution.
In the case of sulfur, experts can use a titration method to determine the concentration of any impurities present in the sample.
.

.
Here are the steps involved in titration for the analysis of impurities in granular sulfur:
1_Sample Preparation: A small amount of the granular sulfur sample is taken and prepared for analysis. The sample is typically dissolved in a solvent to form a solution.
.
2_Selection of Standard Solution: A standard solution of a known concentration is selected that can react with the impurities present in the sample. The most commonly used titrant in the analysis of sulfur impurities is iodine, which reacts with sulfur-containing impurities to form iodide ions.
.
3_Titration: The standard solution is added slowly to the sample solution while stirring until the reaction between the standard solution and the impurities is complete. The endpoint of the reaction is typically detected using an indicator that changes color when the reaction is complete.
.
4_Calculation: The volume of the standard solution required to react with the impurities in the sample is measured. From this, the concentration of impurities in the sample can be calculated.
.
5_Identification of Impurities: By comparing the concentration of impurities in the sample to the expected concentration of impurities in pure sulfur, experts can identify the presence of any impurities in the sample.
.
Overall, titration can provide valuable information on the concentration of impurities in granular sulfur, helping experts to determine its purity.
.
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy techniques such as infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy can be used to analyze the molecular structure of the sulfur sample. By comparing the spectra of the sample to known spectra of pure sulfur, experts can determine the purity of the sample.
Here are the steps involved in spectroscopy for the analysis of granular sulfur:
.
1_Sample Preparation: A small amount of the granular sulfur sample is taken and prepared for analysis. The sample is typically ground into a fine powder and placed in a sample holder.
.
2_Instrument Setup: A spectroscopy instrument, such as an infrared (IR) or Raman spectrometer, is set up to analyze the sample. The instrument is calibrated and the appropriate parameters, such as the wavelength range and resolution, are selected.
.
3_Spectrum Acquisition: The sample is analyzed using the spectroscopy instrument, and a spectrum is obtained that shows the absorption or scattering of light as a function of wavelength. The spectrum provides information on the molecular structure of the sample.
.
4_Comparison to Known Spectra: The obtained spectrum is compared to known spectra of pure sulfur to determine the purity of the sample. The comparison may be qualitative, where the overall shape and features of the spectra are compared, or quantitative, where the intensity of specific peaks in the spectra are analyzed.
.
5_Identification of Impurities: By comparing the spectra of the sample to the expected spectra of pure sulfur, experts can identify the presence of any impurities in the sample.
.
Which Of The Mentioned Sulfur Purity Analysis Methods Is The Best?
There is no one "best" method for determining the purity of sulfur, as different methods may be more appropriate depending on the specific sample being analyzed and the analytical requirements. Each method has its own advantages and limitations.
.
For example, melting point analysis is a quick and easy method to perform but may not be able to detect impurities at very low concentrations.
Elemental analysis can provide quantitative measurements of the elemental composition of the sample, but may not be sensitive to certain impurities or contaminants.
Spectroscopy techniques can provide information on the molecular structure of the sample, but may require specialized equipment and expertise.
Therefore, the most appropriate method for determining the purity of sulfur depends on the specific needs and limitations of the analysis. Often, a combination of methods may be used to obtain a more comprehensive picture of the purity of the sulfur sample.
