.
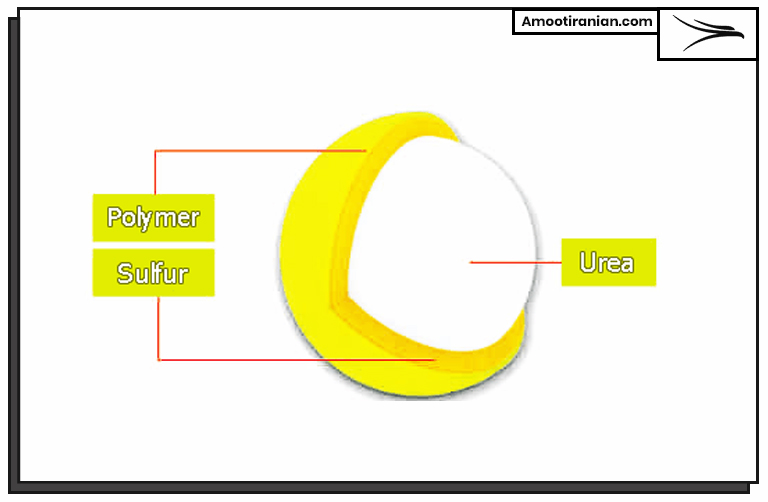
Sulfur coated urea is a slow-release fertilizer, releasing nitrogen gradually into the soil.
It causes more output, low nitrogen loss, & improved crop yields.
.
.
What Is Sulfur Coated Urea?
Sulfur coated urea (SCU) is a type of controlled-release fertilizer that is produced by coating prills of urea with a layer of elemental sulfur.
.
The sulfur coating acts as a semi-permeable barrier that regulates the release of nitrogen from the urea, slowing down the rate of nitrogen release and reducing the risk of:
- leaching
- volatilization
- denitrification
.
This results in improved nutrient use efficiency and reduced environmental impact, making SCU a popular choice for fertilization in agriculture, horticulture, and turf management.
.

.
.
What Is the Formula for Sulfur Coated Urea?
The formula for sulfur coated urea is the same as for regular urea, which is CON2H4 or (NH2)2CO.
.
The only difference is that in sulfur coated urea, a layer of sulfur is added to the surface of the urea granules.
The sulfur serves as a slow-release coating that controls the release of nitrogen over time.
.
What Is the Main Reason for Coating of Urea?
The main reason for coating urea is to regulate its release of nitrogen into the soil.
.
Uncoated urea releases nitrogen rapidly when applied to the soil, which can lead to nutrient losses through leaching, volatilization, and denitrification.
By coating urea with a material like sulfur, the release of nitrogen can be slowed down and controlled, resulting in improved nutrient use efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
The coating can also protect the urea from moisture and other environmental factors, ensuring that the nitrogen is available to plants when they need it most.
.
How Is Sulfur Coated Urea Produced?
Sulfur coated urea (SCU) is produced by coating prills of urea with a layer of elemental sulfur.
.
The production process typically involves the following steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Urea prills are prepared by spraying liquid urea into a prilling tower, which causes the urea droplets to solidify into small, round particles. |
| 2 | Sulfur is melted and heated to a specific temperature, typically around 135°C (275°F). |
| 3 | The urea prills are fed into a rotating drum, which is heated to the same temperature as the molten sulfur. |
| 4 | The molten sulfur is sprayed onto the surface of the rotating urea prills in the drum. The heat from the drum causes the sulfur to solidify and adhere to the surface of the urea prills. |
| 5 | The coated urea prills are removed from the drum and allowed to cool. |
| 6 | The sulfur-coated urea prills are screened to remove any oversized or undersized particles, and then bagged or stored for later use. |
.
It’s worth noting that the specific production process can vary depending on the manufacturer and the equipment used, but these steps provide a general overview of how sulfur coated urea is typically produced.
.
What Is Sulfur Coated Urea Used for?
Sulfur coated urea (SCU) is primarily used as a controlled-release fertilizer in agriculture, horticulture, and turf management.
.
The slow-release properties of SCU make it an effective way to provide a steady supply of nitrogen to crops and plants over an extended period, while minimizing the risk of nutrient loss and environmental damage. Some specific uses of SCU include:
| Application | Description |
| Field crops | SCU is commonly used in the production of field crops such as corn, wheat, soybeans, and cotton. It can be applied pre-plant or as a top-dress application to provide a long-lasting source of nitrogen throughout the growing season. |
| Vegetable and fruit crops | SCU is used in the production of vegetables and fruit crops such as tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, strawberries, and blueberries. Its slow-release properties ensure that nitrogen is available to the plants when they need it most, promoting healthy growth and high yields. |
| Ornamentals | SCU can be used to fertilize a wide range of ornamental plants, including flowers, shrubs, and trees. Its slow-release properties make it an effective way to promote healthy growth and flowering without the risk of fertilizer burn. |
| Turf management | SCU is a popular choice for fertilizing golf courses, sports fields, and other turf areas. Its slow-release properties provide a long-lasting source of nitrogen, while minimizing the risk of damage to sensitive turfgrass species. |
| Landscape maintenance | SCU can be used to fertilize lawns, gardens, and other landscaped areas. Its slow-release properties make it an effective way to promote healthy growth and reduce the need for frequent applications of fertilizer. |
.
It’s worth noting that the specific uses of SCU can vary depending on factors such as soil type, climate, and crop or plant species. It’s important to consult with a qualified agronomist or horticulturist to determine the best fertilizer program for a specific situation.
.
Benefits of Sulfur Coated Urea
There are several benefits of using sulfur coated urea (SCU) as a fertilizer:
| Benefit | Description |
| Controlled release of nitrogen | SCU releases nitrogen slowly over time, providing a steady supply of nutrients to crops and plants, which helps avoid the rapid nitrogen release that can occur with uncoated urea, reducing nutrient loss and environmental damage. |
| Increased nutrient use efficiency | SCU can improve nutrient use efficiency by reducing the amount of nitrogen that is lost through leaching, volatilization, and denitrification, allowing more of the nitrogen to be available to the plants for better growth and yields. |
| Reduced environmental impact | SCU can reduce the risk of nitrogen runoff and leaching, which can contribute to water pollution and other environmental problems, by releasing nitrogen slowly and in a controlled manner. |
| Longer lasting effect | SCU has a slow release property that results in a longer lasting effect compared to traditional fertilizer, reducing the need for frequent applications and lowering overall fertilizer costs. |
| Reduced risk of fertilizer burn | SCU is less likely to cause fertilizer burn, which can occur when too much nitrogen is applied at once, causing damage to plant roots and leaves. |
.
It’s important to note that these benefits can vary depending on factors such as soil type, climate, and crop or plant species. It’s always a good idea to consult with a qualified agronomist or horticulturist to determine the best fertilizer program for a specific situation.
.
Is Sulfur Coated Urea an Economic Choice?
Sulfur coated urea (SCU) can be an economic choice for some agricultural applications, depending on various factors such as:
- crop type
- soil conditions
- climate
.
SCU can be more expensive than traditional urea fertilizer due to the added cost of the sulfur coating process.
However, the slow-release properties of SCU can result in reduced fertilizer costs over time by reducing the frequency of fertilizer applications and increasing nutrient use efficiency.
.
Additionally, the reduced risk of nutrient loss and environmental damage can help protect long-term soil health, which can have economic benefits for farmers in terms of improved crop yields and reduced input costs.
Ultimately, the economic viability of SCU will depend on a range of factors specific to each situation, and it’s important to consult with a qualified agronomist or agricultural economist to determine the best fertilizer program for a given situation.
.
Does Sulfur Coated Urea Have Any Disadvantage?
.
Possible Disadvantages of Sulfur Coated Urea |
| Limited availability in some areas |
| Slow release may not be desirable in all situations |
| Sulfur can acidify soil |
| Not suitable for all crops |
It’s important to note that the disadvantages of SCU will depend on specific factors such as:
- the crop being grown
- soil conditions
- climate
.
These factors should be considered when determining whether SCU or another type of fertilizer is the best choice for a given situation.
.
