.
.
.
What Is the Composition of Urea Fertilizer?
.
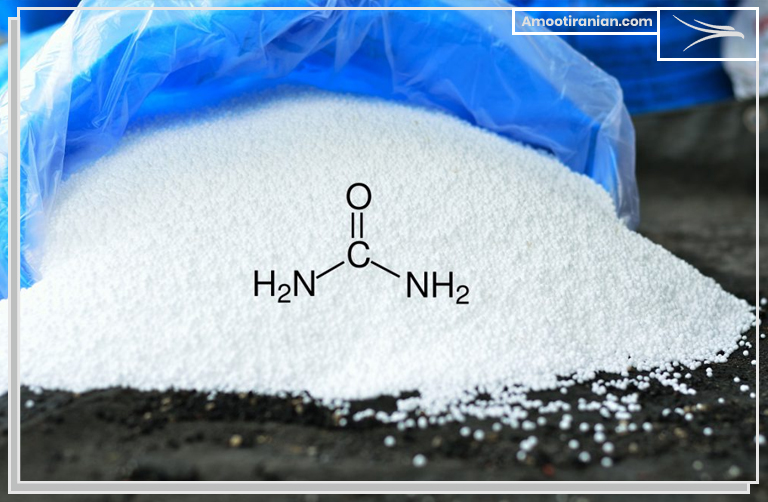
Urea fertilizer is a commonly used nitrogen fertilizer and has the chemical formula CO(NH2)2.
.
It is a white, crystalline substance that contains approximately 46% nitrogen. Urea is synthesized from ammonia and carbon dioxide and is produced as prills or granules depending on the intended use.
In addition to nitrogen, urea fertilizer may contain small amounts of other nutrients, such as phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, and micronutrients, depending on the specific formulation.
These additional nutrients are added to improve plant growth and yield.
.
It’s important to note that urea fertilizer can be harmful if not used properly, as excess nitrogen can lead to environmental pollution and damage to plants.
Therefore, it’s essential to follow the recommended application rates and timing for urea fertilizer to ensure optimal plant growth and minimize negative impacts on the environment.
.
Urea fertilizer is typically sold in bags or bulk, and the specific composition may vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended use.
However, the majority of urea fertilizer contains around 46% nitrogen, which makes it one of the highest nitrogen-content fertilizers available.
The high nitrogen content of urea fertilizer makes it ideal for promoting vegetative growth in plants, such as increased leaf growth and overall plant size.
However, it is important to note that urea fertilizer should not be used as the sole source of nutrients for plants, as it lacks other essential nutrients like potassium and phosphorus.
.
To use urea fertilizer, it should be applied evenly across the soil surface and then worked into the soil to ensure proper distribution.
It’s essential to water the plants after applying the fertilizer to help dissolve the urea and move the nutrients into the root zone, where they can be taken up by the plant.
.
In summary, the composition of urea fertilizer is primarily nitrogen, with small amounts of other nutrients added depending on the intended use.
Proper application and timing of urea fertilizer can help promote healthy plant growth, but it is essential to use it in moderation and in combination with other essential nutrients to avoid negative impacts on the environment and the plant itself.
.
What Is the Main Chemical Component of Urea?
.
The main chemical component of urea is the molecule CO(NH2)2, which is also known as carbamide.
.
It is a colorless, odorless, and highly soluble organic compound that contains two amide functional groups (-NH2) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O).
.
Urea is a naturally occurring compound that is found in the urine of mammals and some other animals.
It is also produced synthetically for use in fertilizers, as well as in the manufacture of plastics, resins, adhesives, and other products.
Urea is a versatile compound that has many important applications in various industries.
For example, in addition to its use as a fertilizer, it is used in the production of animal feed, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products.
It is also used as a reducing agent in diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) to reduce emissions of nitrogen oxides from diesel engines.
.
Overall, the unique chemical properties of urea make it an essential component in many different products and processes, and its versatility and wide range of applications have made it a vital part of modern industry and agriculture.
.
What Is the Percentage Composition of Urea?
The percentage composition of urea is as follows:
- Carbon: 46.65%
- Nitrogen: 46.65%
- Oxygen: 6.70%
.
This means that, by mass, urea is composed of approximately 46.65% carbon, 46.65% nitrogen, and 6.70% oxygen.
It’s important to note that the percentage composition may vary slightly depending on the purity of the urea sample and the specific production method used.
Additionally, some formulations of urea fertilizer may contain small amounts of other nutrients or additives, which can affect the percentage composition.
.
What Is Pure Urea Made of?
.
Pure urea is a crystalline organic compound that is composed of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms.
.
The molecular formula of pure urea is CO(NH2)2, which means it contains two amide functional groups (-NH2) and one carbonyl group (C=O).
Pure urea is typically produced synthetically from ammonia and carbon dioxide in a process known as the Haber-Bosch process.
The process involves reacting ammonia and carbon dioxide under high pressure and temperature to produce ammonium carbamate, which is then dehydrated to form urea.
The resulting pure urea is a white, odorless, and water-soluble solid that is commonly used in the production of fertilizers, resins, adhesives, and other products.
However, it is important to note that while pure urea is relatively safe, it can be hazardous if ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and proper safety precautions should be taken when handling it.
.
How Much CO2 Is in Urea?
Urea (CO(NH2)2) contains two carbon atoms, but it does not contain any carbon dioxide (CO2) molecules as part of its chemical structure.
However, carbon dioxide is involved in the industrial production of urea through the Haber-Bosch process.
In the Haber-Bosch process, ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are reacted under high temperature and pressure to produce ammonium carbamate, which is then dehydrated to form urea.
During this process, one molecule of CO2 is used for every molecule of urea produced.
Therefore, the amount of CO2 used to produce urea depends on the quantity of urea being produced.
For example, to produce one metric ton of urea, approximately 1.5 metric tons of carbon dioxide are used. This makes the production of urea a significant source of carbon dioxide emissions and contributes to the carbon footprint of the fertilizer industry.
.
Is Urea Full of Nitrogen?
.
.
Why is urea 46?
Yes, urea is a nitrogen-rich compound. It is one of the most concentrated sources of nitrogen used in agriculture and gardening.
Urea contains approximately 46% nitrogen by weight, which is the highest nitrogen content among dry fertilizers.
This high nitrogen content makes urea an effective and popular choice for promoting vegetative growth in plants, such as increased leaf growth and overall plant size.
However, it is important to note that while urea is a valuable source of nitrogen, it does not contain other essential plant nutrients such as phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients.
Therefore, urea should be used in combination with other fertilizers to provide a balanced and comprehensive nutrient supply for plants.
Additionally, excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers like urea can have negative environmental impacts, such as:
.
How Much Nitrogen Is in 1 kg of Urea?
.
One kilogram of urea contains approximately 0.468 kilograms (or 468 grams) of nitrogen.
.
This is because urea has a molecular weight of 60.06 g/mol and contains two nitrogen atoms per molecule, which corresponds to a nitrogen content of 46.65% by weight.
Therefore, one kilogram of urea contains approximately 0.4665 kg of nitrogen (or 466.5 grams).
.
Is Urea an Organic Fertilizer?
Urea is considered a synthetic or inorganic fertilizer, rather than an organic fertilizer.
This is because urea is not derived from plant or animal materials, but rather it is synthesized chemically from ammonia and carbon dioxide.
However, it is worth noting that urea is a naturally occurring compound that is found in urine and other organic materials, and it can be broken down into other organic compounds by soil microorganisms.
.
In contrast, organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources, such as plant and animal waste, and are often minimally processed.
Organic fertilizers provide nutrients to plants in a slower and more sustainable manner than synthetic fertilizers, as the nutrients are released gradually through the breakdown of organic matter by soil microorganisms.
.
While urea is not considered an organic fertilizer, it can be a useful component of a balanced fertility program when used in combination with other organic fertilizers, such as compost or animal manure.
This can help provide a comprehensive nutrient supply to plants while also promoting healthy soil biology and minimizing negative environmental impacts.
.

Writer: Amin Kamali
Sales Specialist at Amoot Iranian Company
