.
Sulfur Physical and Chemical Properties
.
1. Sulfur Physical Properties
Sulfur is a non-metallic element that is abundant in the earth’s crust and has a variety of physical properties.
It is a solid at room temperature, with a melting point of 115.21°C and a boiling point of 444.6°C.
.

.
Sulfur has a characteristic bright yellow color and is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as carbon disulfide. It has a low density of 2.07 g/cm³ and is a poor conductor of electricity and heat.
Sulfur also exhibits allotropy, which means that it can exist in different forms with different crystal structures and physical properties, including rhombic sulfur, monoclinic sulfur, plastic sulfur, and amorphous sulfur.
.
.
2. Sulfur Chemical Properties
Sulfur has a variety of chemical properties due to its ability to form a wide range of compounds with other elements.
It is highly reactive and can react with many metals, non-metals, and organic compounds to form a variety of sulfides, sulfates, and other compounds.
Sulfur burns in air to form sulfur dioxide, a gas that is a major contributor to acid rain. It also reacts with halogens such as chlorine and fluorine to form sulfur halides, and with nitrogen to form sulfur nitrides.
Sulfuric acid, a highly corrosive and strong acid, is one of the most important and widely used sulfur compounds in industry, and is used in the production of fertilizers, detergents, and many other products.
Sulfur also has a variety of biological functions and is an essential element in the human body, where it is involved in the formation of proteins and other important molecules.
.

.
.
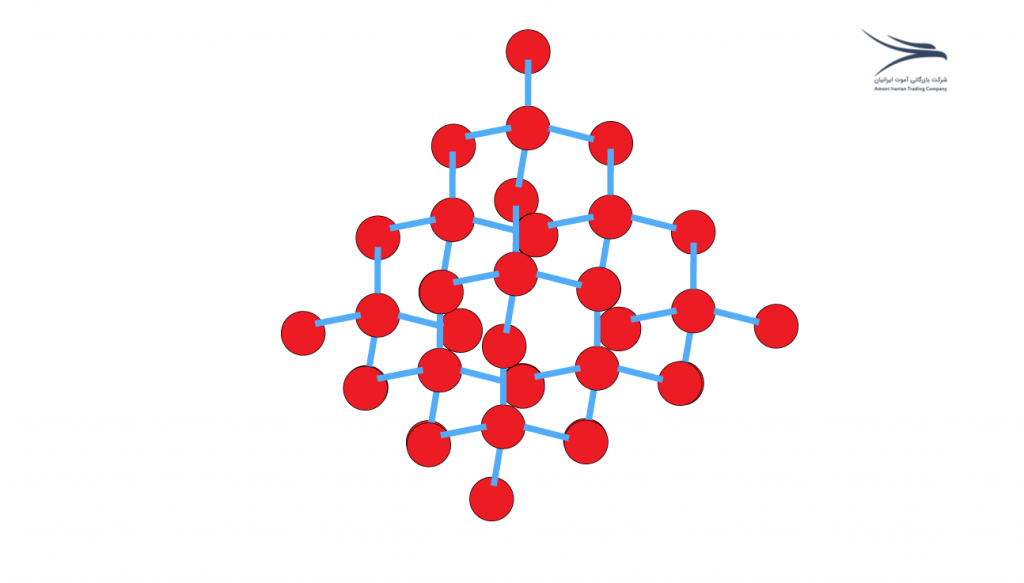
What Is Allotropy?
The term “allotropic” or “allotropy” refers to the property of some chemical elements to exist in different forms or structures, called allotropes, under different conditions of temperature and pressure.
Allotropy arises from the fact that atoms of an element can arrange themselves in different ways to form different molecules or crystal structures, giving rise to different physical and chemical properties for each allotrope.
.
.
What Is Sulfur Allotropic Form?
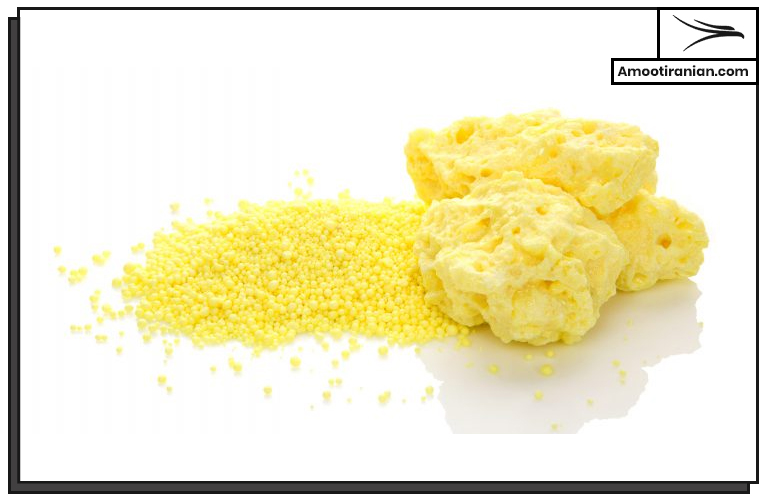
Sulfur allotropes are different structural forms or arrangements of sulfur atoms in which the atoms are bonded together in different ways.
Sulfur is a chemical element that has many allotropes, and each allotrope has unique physical and chemical properties.
For example, some allotropes of sulfur are crystalline and have different colors, while others are amorphous and have a rubber-like texture.
.

.
The properties and uses of sulfur allotropes and compounds depend on their specific structures and chemical properties, which can vary widely.
Overall, the study of sulfur allotropes and their properties is an important area of research in chemistry and materials science.
Sulfur allotropes are important in many applications, including the production of sulfuric acid, fertilizers, and rubber, as well as in the manufacture of gunpowder and other explosives.
.
How Many Allotropes of Sulfur Are There?
There are several Sulfur Allotropic Forms, but the most common are:
.
Sulfur Allotropes
| Allotrope | Name | Description |
| 1. | Rhombic sulfur | Most stable and common allotrope, yellow crystals or powder, also known as α-sulfur |
| 2. | Monoclinic sulfur | Less stable than rhombic sulfur, also known as β-sulfur |
| 3. | Plastic sulfur | Transparent to opaque, elastic and rubbery in texture |
| 4. | Amorphous sulfur | Brown or black powder, without a definite shape or structure |
| 5. | Cyclo-octasulfur | Crown-shaped molecule consisting of eight sulfur atoms arranged in a ring |
| 6. | γ-sulfur | Red or orange in color, unstable at room temperature, converted to rhombic sulfur upon heating |
| 7. | ε-sulfur | Gray, metallic-looking solid, stable at high pressure and temperature |
| 8. | ζ-sulfur | Dense, black, metallic-looking solid, stable at high pressure and temperature |
| 9 | λ-sulfur | Highly reactive allotrope, formed at low temperatures and high pressures |
| 10 | μ-sulfur | Chain-like molecular structure of sulfur |
| 11. | ν-sulfur | Helical molecular structure of sulfur |
| 12. | π-sulfur | Polymerized allotrope of sulfur |
| 13. | ρ-sulfur | Glassy and brittle allotrope of sulfur |
| 14. | σ-sulfur | Molecular sulfur with an S-S bond |
| 15. | τ-sulfur | High-temperature allotrope of sulfur, stable above 1000°C |
| 16. | χ-sulfur | Crystalline and metastable allotrope of sulfur, formed at high temperatures and pressures |
| 17. | Clathrate sulfur | Cage-like structure of sulfur atoms trapping other molecules |
| 18. | M2S sulfur | Quenched alloy of sulfur and metals, such as tin and copper |
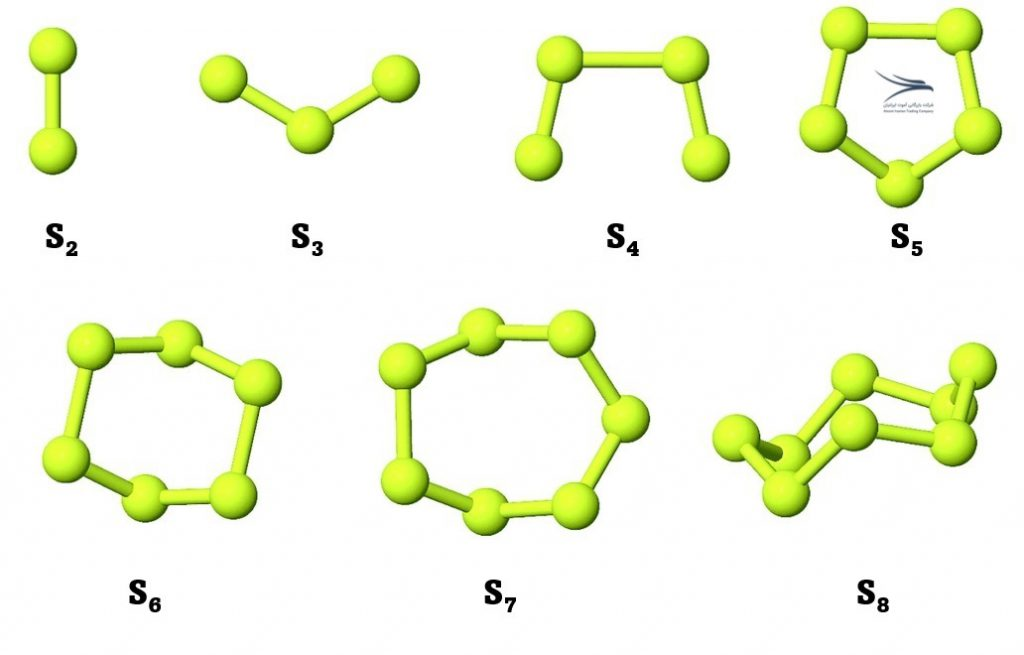
| 19. | S3, S4, S5, S7, S8 | Cyclo-sulfur molecules consisting of 3, 4, 5, 7, and 8 sulfur atoms respectively |
.
.
What Is the Most Common Sulfur Allotrope?
The most common sulfur allotrope is rhombic sulfur, also known as α-sulfur. It is the stable form of sulfur at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and it typically appears as yellow crystals or powder.
The other allotropes of sulfur are either less stable or require specific conditions to form.
Rhombic sulfur allotrope was discovered in 1759 by Antoine Lavoisier, a French chemist.
.
What Is the Most Stable Form of Sulfur?
The most stable form of sulfur is rhombic sulfur, also known as α-sulfur. It is the form of sulfur that occurs naturally and is the most commonly found allotrope of sulfur.
Rhombic sulfur is stable at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and it typically appears as yellow crystals or powder.
.
Is S2 an Allotropic Form of Sulfur?
.
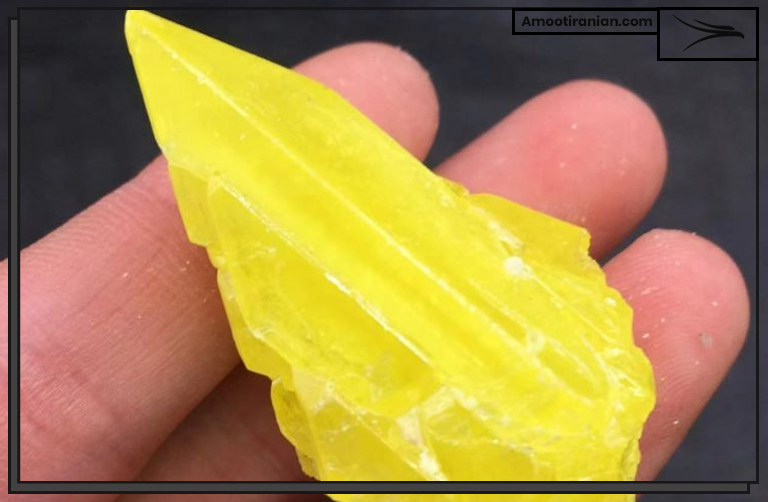
S2 is not considered an allotropic form of sulfur.
.
S2 is actually a molecule composed of two sulfur atoms bonded together by a covalent bond. This molecule is also known as sulfur gas or diatomic sulfur.
Sulfur allotropes, on the other hand, are different structural forms or arrangements of sulfur atoms in which the atoms are bonded together in different ways to form molecules or crystal structures.
Examples of sulfur allotropes include rhombic sulfur, monoclinic sulfur, plastic sulfur, amorphous sulfur, and cyclic forms such as S8.
So, while S2 does contain sulfur atoms, it is not considered an allotrope of sulfur because it is a discrete molecule and not a form of solid sulfur with a distinct crystal structure.
.

.
Is S8 the Allotropic Form of Sulphur?
.
Yes, S8 is one of the most well-known and common allotropic forms of sulfur.
.
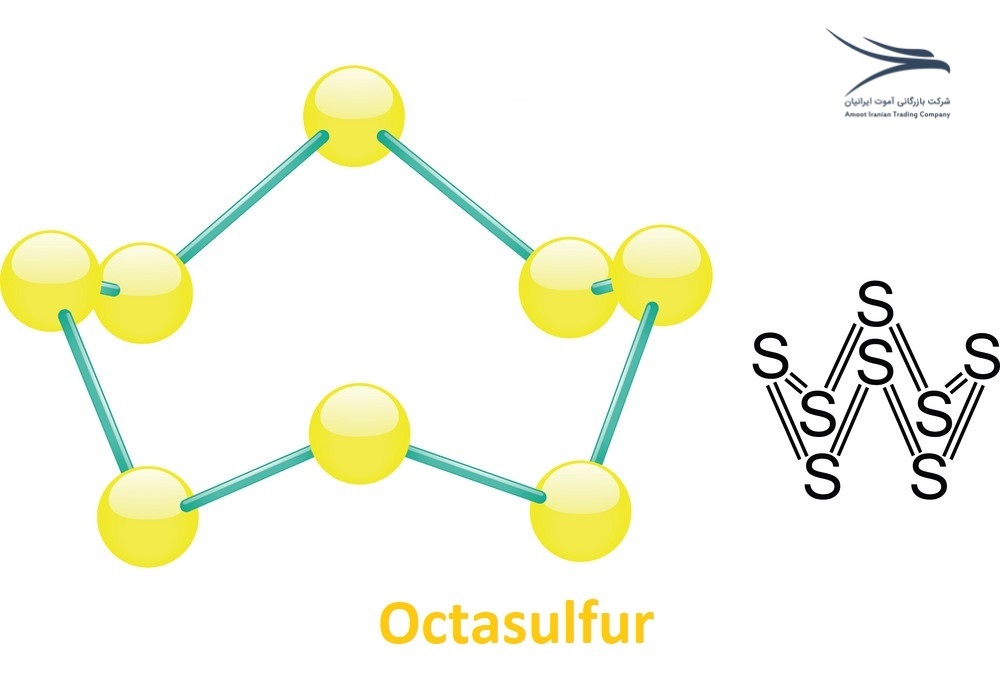
S8 is an allotrope of sulfur consisting of eight sulfur atoms arranged in a crown-shaped ring. This form of sulfur is also known as octasulfur or cyclo-octasulfur.
.
.
.
S8 is a bright yellow crystalline solid that is insoluble in water and has a melting point of 115.21°C. It is stable at room temperature and atmospheric pressure and is commonly used in the production of sulfuric acid, vulcanization of rubber, and as a pesticide and fungicide.
S8 is just one of many allotropic forms of sulfur, and depending on the conditions of temperature and pressure, sulfur can exist in a variety of different allotropes, each with unique physical and chemical properties.
