
.
Does Oil Have Sulfur?
Yes, crude oil typically contains sulfur compounds, which are naturally occurring impurities in the oil. The amount of sulfur present in crude oil can vary widely depending on the source and location of the oil.
Some types of crude oil, such as sour crude, can have very high levels of sulfur, while others, such as sweet crude, have lower sulfur content. The sulfur content of crude oil is an important factor in the refining process, as it affects the quality and properties of the resulting refined products.
When crude oil is processed in a refinery, one of the main goals is to remove the sulfur compounds from the oil in order to produce cleaner-burning fuels with lower emissions of sulfur dioxide and other harmful pollutants.
This is typically done through a process called hydrodesulfurization (HDS), which involves reacting the fuel with hydrogen gas at high temperature and pressure in the presence of a catalyst to remove the sulfur compounds from the oil.
In recent years, regulations have been implemented in many countries to limit the amount of sulfur allowed in fuels, with the goal of reducing air pollution and improving public health.
For example, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has implemented a global sulfur cap on marine fuels, limiting the sulfur content of marine fuels to 0.5% by mass, down from the previous limit of 3.5%.
The development of cleaner-burning fuels with lower sulfur content has been an important focus for the oil and gas industry in recent years, with many refineries investing in new technologies and processes to reduce sulfur emissions and comply with regulations.
Additionally, alternative fuels such as natural gas, biofuels, and electric vehicles are being developed as potential solutions to reduce the environmental impact of transportation.
Why Is Sulfur Removed from Oil?
Sulfur is removed from oil to meet regulations set by governments to reduce sulfur-related air pollution.
When fuels containing sulfur are burned, they release sulfur dioxide, which can contribute to acid rain, respiratory problems, and other environmental issues. To reduce these negative effects, the level of sulfur in fuels is regulated, and refineries must remove sulfur from fuels during the refining process.
The primary method used to remove sulfur from crude oil-derived fuels is hydrodesulfurization (HDS).
This process involves reacting the fuel with hydrogen gas at high temperature and pressure in the presence of a catalyst to remove organic sulfur compounds from the fuel. The sulfur compounds are converted to hydrogen sulfide, which is then removed from the fuel through further processing.
By removing sulfur from fuels, refineries can produce cleaner burning fuels that have lower emissions of sulfur dioxide and other harmful pollutants.
However, the process of removing sulfur can be energy-intensive and costly, and there is ongoing research into developing more efficient and sustainable methods for sulfur removal.
Where Is The Removed Sulfur Used in?
The sulfur that is removed from oil during the refining process is often used to produce sulfuric acid, which is a highly important industrial chemical used in a wide range of applications, including fertilizer production, metal processing, and the production of chemicals and detergents.
Sulfur can also be recovered from the hydrodesulfurization process and sold as a byproduct to be used in other industries or applications.
Amoot Iranian Trading Company supplies sulfur of Turkmenistan, which is extracted from oil and gas.
Over 20 years experience in exporting sulfur to numerous countries across the globe has made Amoot a reliable and well-known company. Arabic and African countries are the main buyers of Amoot’s sulfur. Knowledgeable staff and engineers of Amoot along with quality and pure products are two other reasons behind the fame of Amoot Company in Middle East.
How Is Sulphur Removed from Crude Oil?
How do refineries remove sulfur?
Here is a simplified step-by-step explanation of how sulfur is removed from crude oil using hydrodesulfurization (HDS):
| Step | Description |
| 1 | Crude oil is heated and vaporized in a furnace. |
| 2 | The vaporized oil is mixed with hydrogen gas in a reactor vessel. |
| 3 | The hydrogen and oil mixture is passed over a catalyst, which typically contains metals such as nickel or cobalt, to initiate the hydrodesulfurization reaction. |
| 4 | The sulfur compounds in the oil react with the hydrogen gas to form hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas. |
| 5 | The H2S gas is removed from the reactor and sent to a sulfur recovery unit, where the H2S is converted into elemental sulfur or sulfuric acid. |
| 6 | The oil and hydrogen mixture is cooled and condensed back into liquid form, and any remaining traces of H2S gas are removed. |
| 7 | The purified oil is further processed and blended with other components to produce various types of fuels, such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. |
Overall, the hydrodesulfurization process is an important step in the refining process that helps to reduce the sulfur content of fuels and improve air quality.
Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons and impurities, including sulfur compounds that can be harmful to the environment and human health when burned. To reduce the level of sulfur in fuels, refineries use a process called hydrodesulfurization (HDS).
.
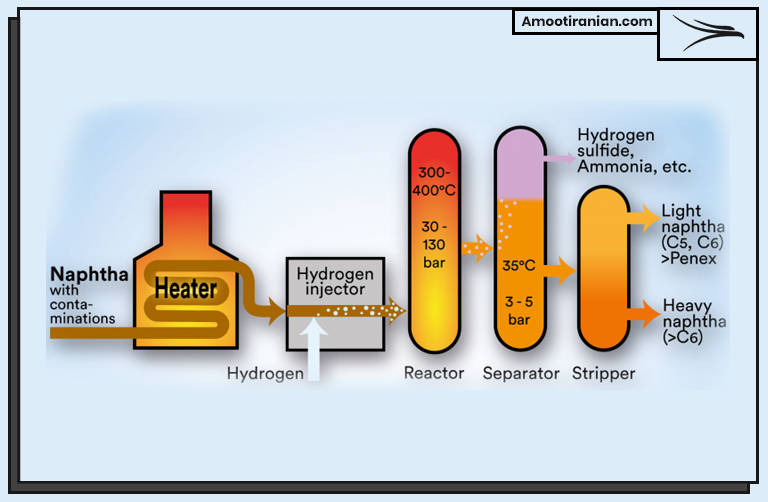
.
As mentioned in the table above, in the first step of the HDS process, crude oil is heated and vaporized in a furnace. The vaporized oil is then mixed with hydrogen gas in a reactor vessel, where it is subjected to high temperature and pressure conditions.
The next step involves passing the hydrogen and oil mixture over a catalyst, which typically contains metals such as nickel or cobalt.
The catalyst acts as a trigger to initiate the hydrodesulfurization reaction, which breaks down the sulfur compounds in the oil and reacts them with hydrogen to form hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas.
.

.
The H2S gas is then removed from the reactor and sent to a sulfur recovery unit, where it is converted into elemental sulfur or sulfuric acid. These products can be sold or reused in other industrial processes.
After the H2S gas is removed, the oil and hydrogen mixture is cooled and condensed back into liquid form.
Any remaining traces of H2S gas are removed, and the purified oil is further processed and blended with other components to produce various types of fuels, such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
Overall, the hydrodesulfurization process is an important step in the refining process that helps to reduce the sulfur content of fuels and improve air quality. By removing sulfur from crude oil, refineries can produce cleaner burning fuels that emit fewer harmful pollutants when burned.
