.
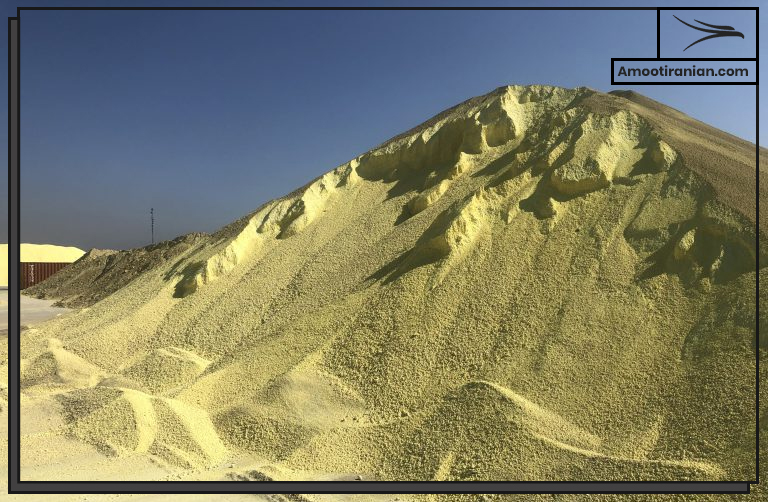
Sulfur is a non-metallic chemical element with the atomic number 16 and the symbol S.
It is found in many minerals, including sulfates and sulfides.

.
.
Sulfur has several chemical properties, including:
.
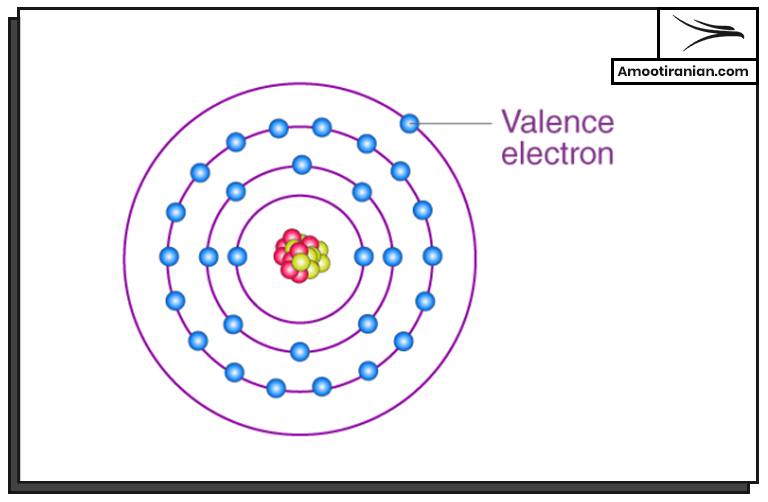
1. Valence
Sulfur has a valence of 2, 4, or 6.
This means that it can form compounds with different oxidation states.
.
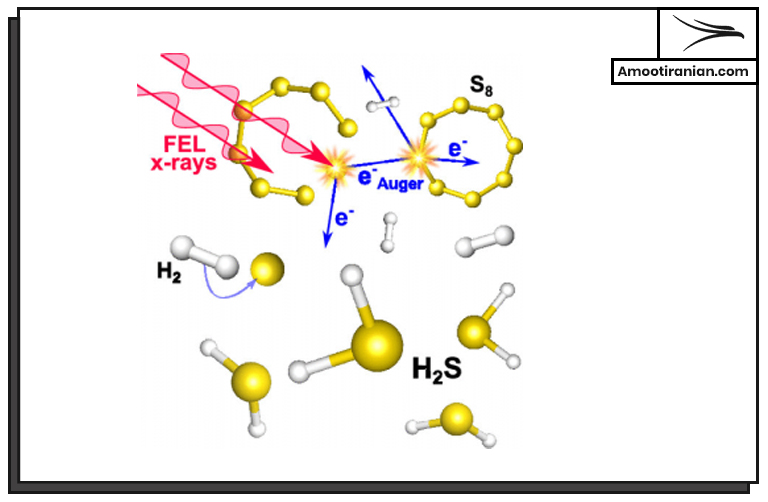
2. Reactivity
Sulfur is a highly reactive element that readily combines with other elements to form a wide variety of compounds.
It reacts with most metals, non-metals, and organic compounds.
.
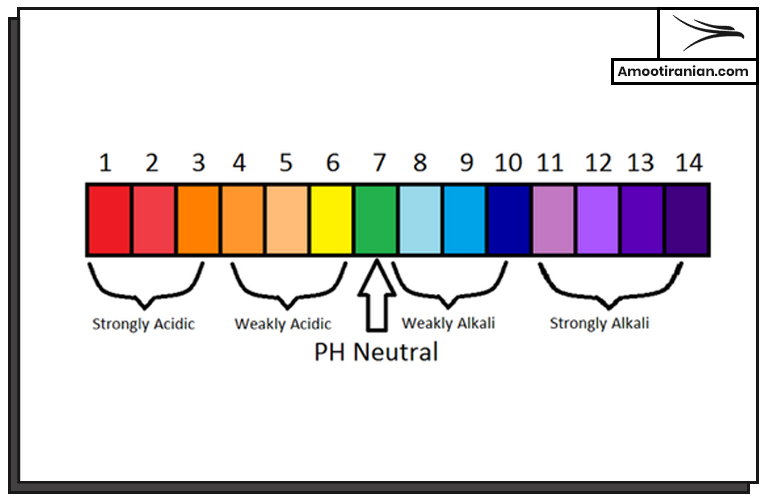
3. Acidic properties
Sulfur is a weakly acidic element that reacts with metals to form sulfides.
It also reacts with bases to form sulfates.
.
4. Oxidation
Sulfur can be oxidized to form sulfur dioxide (SO2) or sulfur trioxide (SO3).
These compounds are used in the production of sulfuric acid.
.
Sulfur is combustible and can burn with a blue flame to produce sulfur dioxide.
It is often used as a component in gunpowder and other explosives.

.
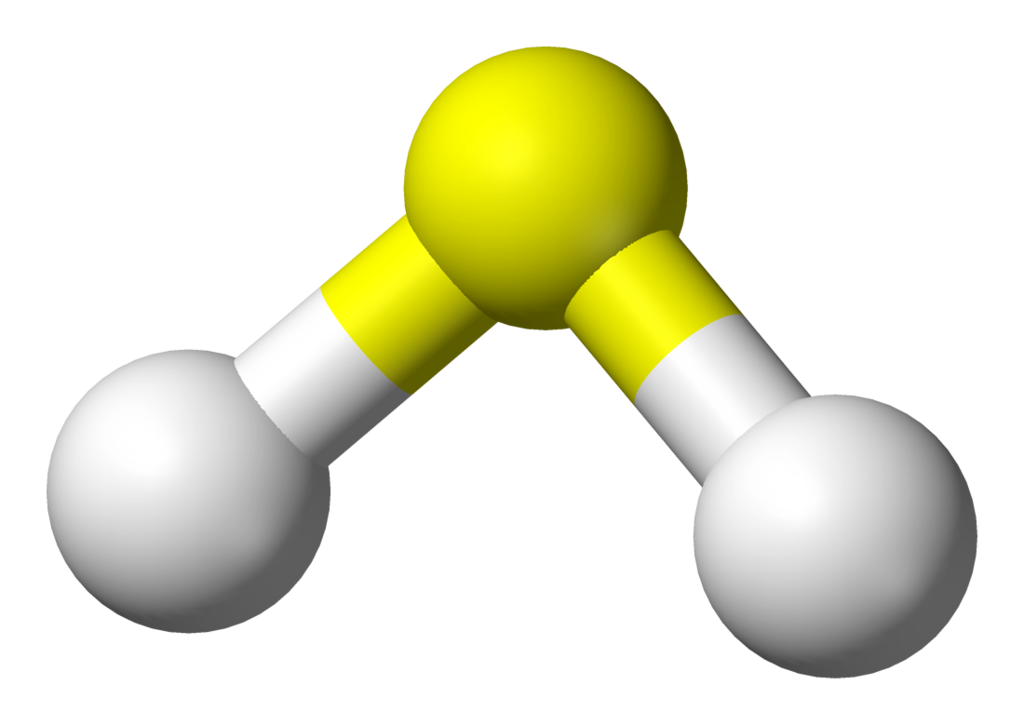
6. Reduction
Sulfur can be reduced to hydrogen sulfide (H2S) by reacting with hydrogen.
This reaction is used in the production of sulfur-containing compounds such as sulfuric acid.
.
7. Polymerization
Sulfur can undergo polymerization to form long chains of sulfur atoms.
This process is used in the production of rubber.
.
8. Allotropy
Sulfur has several allotropes, which are different forms of the same element with different physical and chemical properties.
The most common allotropes of sulfur are rhombic sulfur and monoclinic sulfur.
.
9. Solubility
Sulfur is insoluble in water.
But it is soluble in many organic solvents such as:
- carbon disulfide
- benzene
.
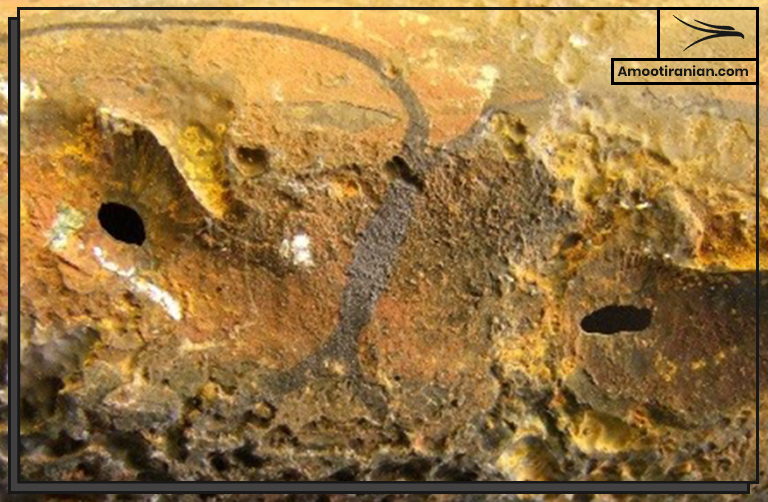
10. Corrosion
Sulfur can cause corrosion in some metals, especially in the presence of water and air.
This is because it can react with metal ions to form metal sulfides.

.
11. Toxicity
Sulfur compounds such as hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide can be toxic to humans and animals at high concentrations.

.
12. Hydrolysis
Sulfur compounds can undergo hydrolysis, which is a chemical reaction with water that breaks down the compound into its constituent ions or molecules.

.
13. Chelation
Sulfur can act as a chelating agent, which means that it can form a complex with a metal ion by surrounding it with a ring of sulfur atoms.
This process is used in medicine to treat metal poisoning.
.
14. Precipitation
Sulfur can form precipitates with certain metals, such as lead and mercury.
This property is used in analytical chemistry to detect these metals in solutions.
.
15. Isotope
Sulfur has four stable isotopes and several radioactive isotopes.
These isotopes are used in radiometric dating and other scientific applications.
.
In conclusion, sulfur is a highly reactive and versatile element with numerous chemical properties.
It has the ability to form compounds with different oxidation states, react with various elements, and undergo different chemical reactions such as:
- oxidation
- reduction
- hydrolysis
.

.
Sulfur has important applications in various industries, including the production of sulfuric acid, rubber, and explosives.
However, it also has toxic and corrosive properties that can pose a risk to human health and the environment.
Overall, understanding the chemical properties of sulfur is crucial for its safe and efficient use in various applications.
